- Home
- Products
- Pathway
- Support
- Contact Us

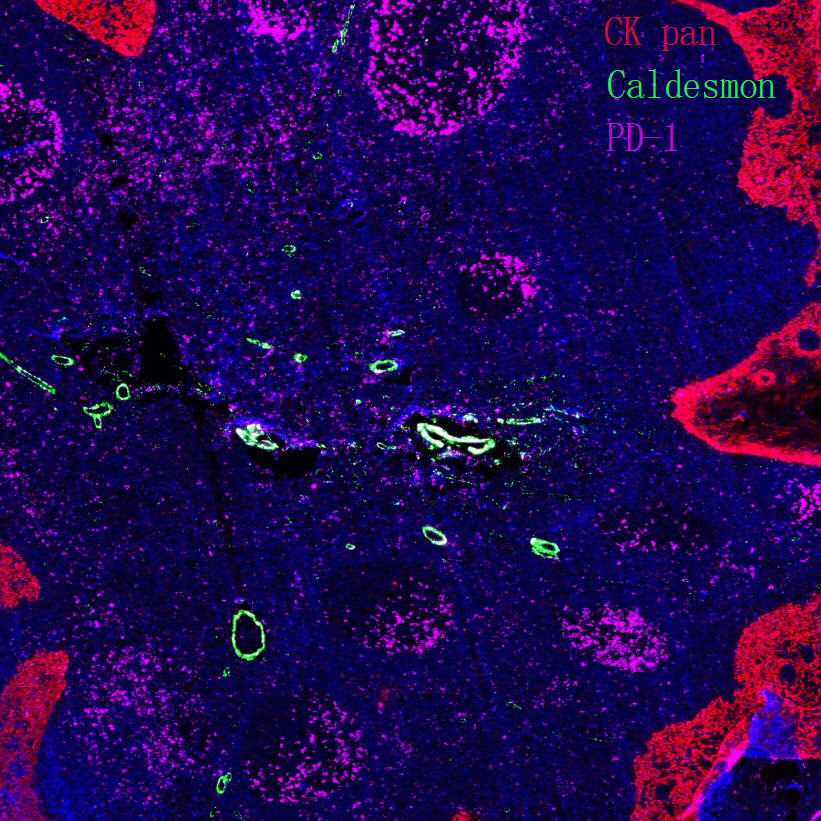
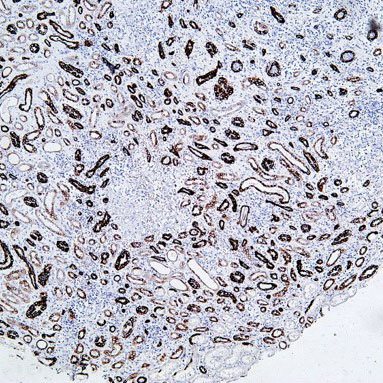
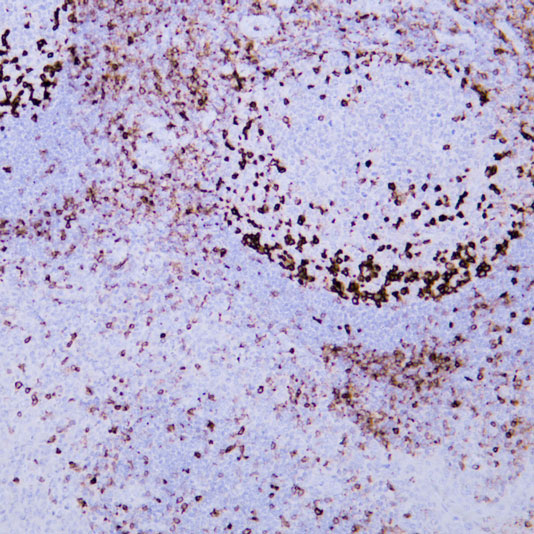
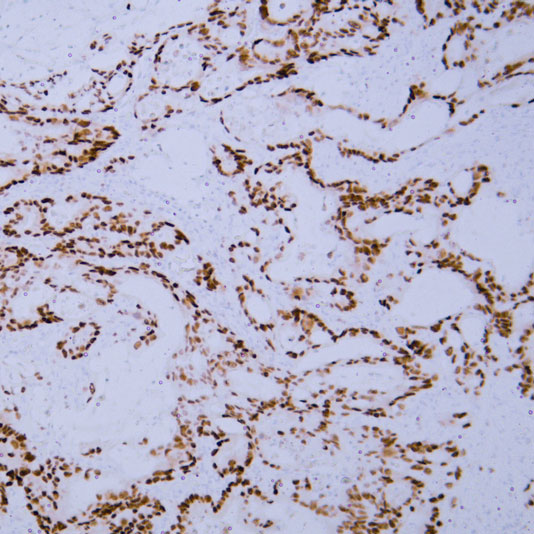
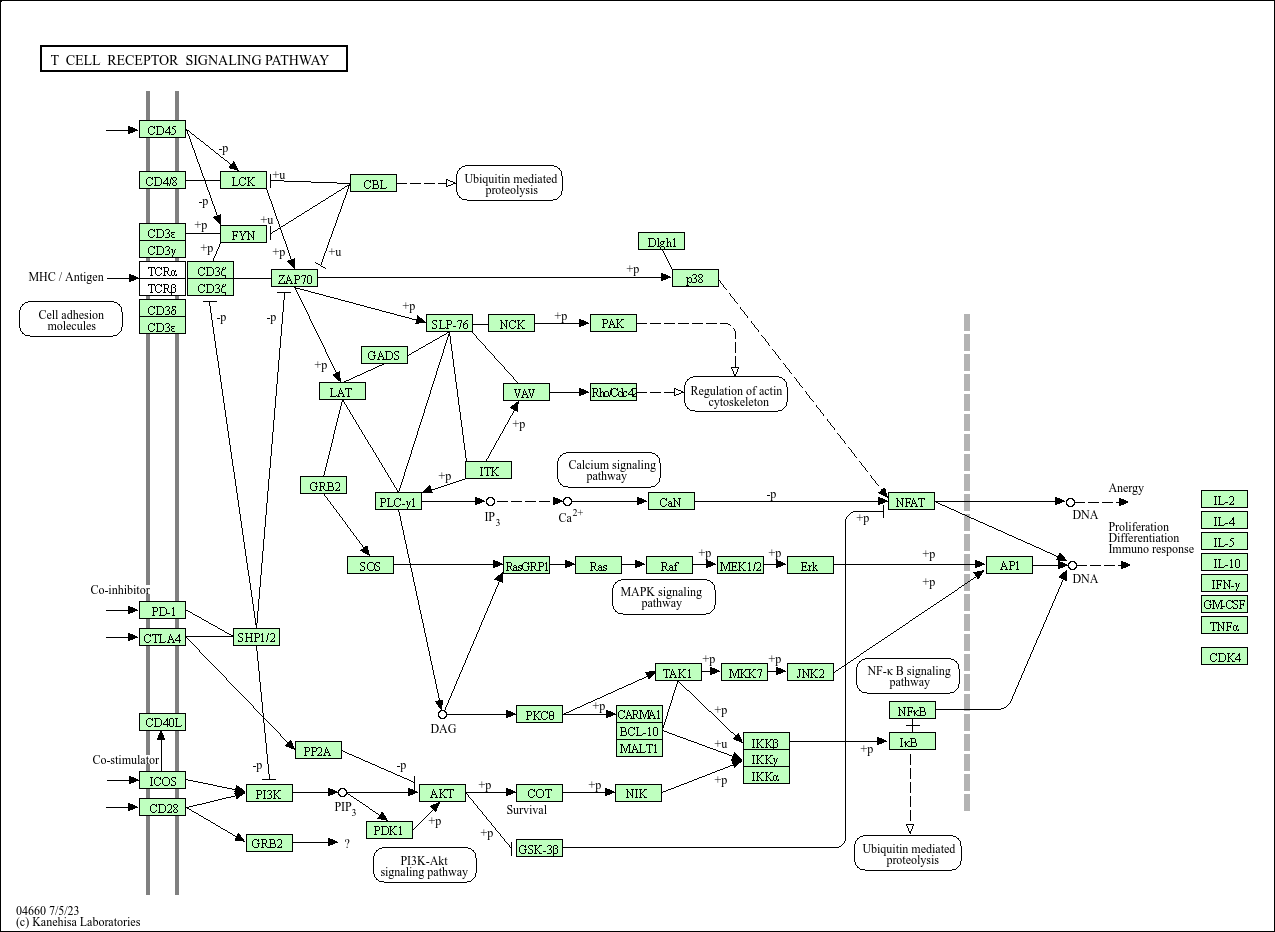
T cell receptor signaling pathway
Core of basic research: As the core pathway of adaptive immunity, it deciphers the molecular mechanism by which TCR recognizes MHC-antigen complexes to initiate T cell activation, proliferation, and differentiation. Upon TCR binding to MHC-antigen peptides, ITAM motifs on the CD3ζ chain are phosphorylated by Lck kinase, recruiting and activating ZAP-70 kinase. ZAP-70 phosphorylates signal adaptor proteins such as LAT and SLP-76, forming a signal complex that activates three core pathways: PLC-γ1-mediated NF-κB activation, Ras-MAPK-mediated AP-1 activation, and PI3K-Akt-mediated cell survival and metabolic activation. Meanwhile, CD28 binding to B7 molecules (CD80/CD86) provides costimulatory signals to prevent T cell anergy. Research focuses on the relationship between immune synapse formation and signal transduction, phosphorylation cascade regulation of signaling molecules, threshold mechanisms of T cell activation, and T cell dysfunction caused by pathway inhibition (e.g., PD-1/PD-L1 binding) in the tumor microenvironment.
Core key proteins: TCR complex (TCRα/β + CD3ζ/δ/ε/γ), Lck, ZAP-70 (tyrosine kinases), LAT, SLP-76 (signal adaptor proteins), PLC-γ1, PI3K, Akt, Ras, Raf, MEK, ERK (MAPK pathway), NF-κB, AP-1 (c-Fos/c-Jun), CD28 (costimulatory molecule), CTLA-4 (negative regulator).
Core key proteins: TCR complex (TCRα/β + CD3ζ/δ/ε/γ), Lck, ZAP-70 (tyrosine kinases), LAT, SLP-76 (signal adaptor proteins), PLC-γ1, PI3K, Akt, Ras, Raf, MEK, ERK (MAPK pathway), NF-κB, AP-1 (c-Fos/c-Jun), CD28 (costimulatory molecule), CTLA-4 (negative regulator).
Product list
-
{{item.title}}{{item.react}}{{item.applicat}}
Product list
Product name
Reactivity
Application
Related Resource Links
Related Promotional Journal Downloads

Explore Our Recommended Popular Products
More products
30,000+ high- quality products available online
Primary Antibodies, Secondary Antibodies, mIHC Kits, ELISA Kits, Proteins, Molecular Biology Products,Cell Lines,Reagents ...
Contact Us