Core Research Directions and Scientific Questions
1. Regulatory Mechanisms of Core Metabolic Pathways
Glucose metabolism regulation: Explore the molecular regulatory networks of core pathways including glycolysis, tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA), and oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS); decipher the signaling mechanisms of cellular metabolic switching (e.g., Warburg effect) under hypoxia (HIF-1α) or nutrient deprivation; and investigate post-translational modification (phosphorylation, acetylation) regulation of key enzymes (e.g., PFK1, LDHA).
Lipid metabolism balance: Study the regulatory logic of fatty acid synthesis (FASN, ACC), breakdown (CPT1, PPARα), and transport (CD36, apoE); clarify the effects of dynamic lipidomic changes (e.g., phospholipids, cholesterol, sphingolipids) on cell membrane homeostasis and signal transduction; and analyze the association between abnormal lipid metabolism and lipotoxicity.
Amino acid metabolism function: Focus on metabolic pathways of glutamine, serine, and tryptophan; reveal their roles in energy supply, biosynthesis (nucleic acids, proteins), and oxidative stress regulation; and explore the signaling molecule functions of metabolic intermediates (e.g., α-ketoglutarate, polyamines).
2. Cell Metabolism and Cell Fate Determination
Metabolic reprogramming and proliferation/differentiation: Decipher metabolic remodeling characteristics of stem cells, immune cells, and tumor cells during fate transition (e.g., glycolysis dependence of stem cells, metabolic differences between M1/M2 macrophage subtypes); clarify the regulation of transcription factors (e.g., MYC, p53) by metabolic enzymes and metabolites; and reveal the molecular mechanisms by which metabolic reprogramming drives cell proliferation and differentiation.
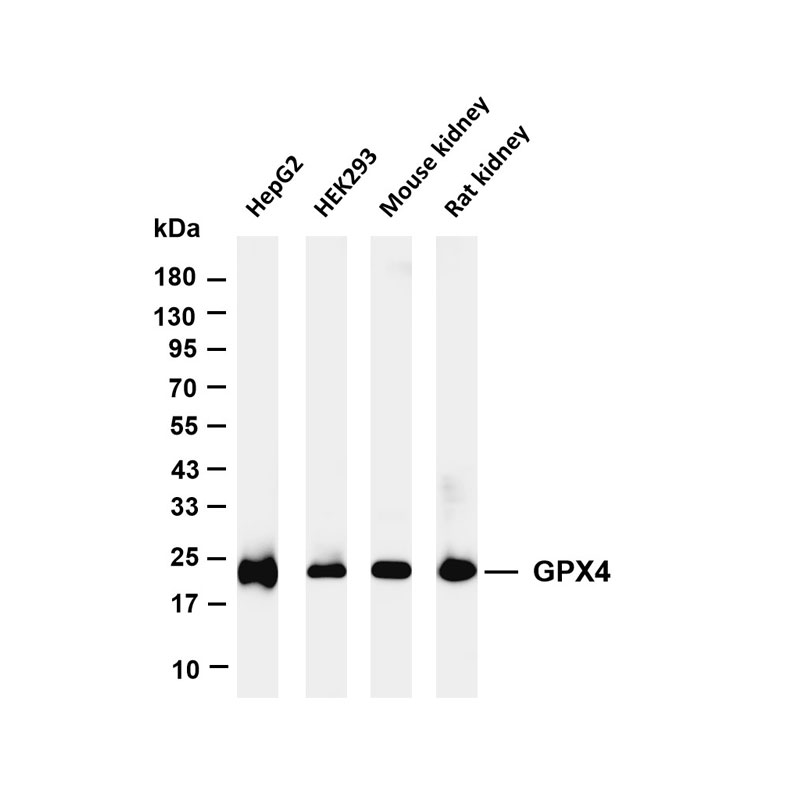
Metabolic imbalance and cell death: Investigate the core mechanisms of metabolic disorders (e.g., ROS accumulation, ATP depletion, lipid peroxidation) triggering cell death modes such as apoptosis, ferroptosis, and cuproptosis; and analyze the regulatory roles of key metabolic enzymes (e.g., GPX4, FDX1) in death pathways.
Metabolic memory and cell homeostasis: Study the "memory" mechanisms of cells to previous metabolic states (e.g., epigenetic modifications); clarify their roles in diabetic complications and tumor recurrence; and the feedback regulatory network for maintaining metabolic homeostasis.
3. Metabolism, Microenvironment, and Cross-Regulation
Intercellular metabolic coupling: Explore the metabolic synergy mechanisms between different cell types in tissue microenvironments (e.g., tumor cells and stromal cells, immune cells and parenchymal cells); and analyze the effects of "metabolic symbiosis" (e.g., lactate shuttle, glutamine exchange) on tissue function.
Metabolism-signaling pathway crosstalk: Clarify the molecular logic of metabolites (e.g., AMP, NAD+, acetyl-CoA) acting as signaling molecules to regulate cellular pathways (AMPK, SIRT1, mTOR); and reveal the integration mechanisms of metabolism with growth and stress pathways.
Microbiome-metabolism interaction: Study the regulation of host cell metabolism by metabolites of gut/skin microbiomes (e.g., short-chain fatty acids, bile acids); and analyze how microbiome dysbiosis affects host health (e.g., obesity, inflammation) via metabolic reprogramming.
4. Metabolic Abnormalities, Diseases, and Aging Mechanisms
Molecular etiology of metabolism-related diseases: Decipher the metabolic mechanisms of diabetes (insulin resistance and GLUT4 transport abnormalities), obesity (lipid metabolism disorder and inflammation activation), and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD, lipid accumulation and hepatocyte damage); and identify key metabolic biomarkers and regulatory targets.
Tumor metabolic reprogramming: Reveal the core mechanisms of tumor cells relying on specific metabolic pathways (e.g., glycolysis, glutamine addiction, enhanced fatty acid synthesis) for unlimited proliferation; analyze the regulation of tumor metabolism by oncogenes/tumor suppressors (e.g., PI3K/Akt, p53); and provide theoretical basis for metabolism-targeted tumor therapy.
Metabolism and aging: Investigate the molecular mechanisms of decreased metabolic rate, mitochondrial dysfunction, and oxidative stress accumulation during aging; analyze the metabolic pathways by which interventions such as calorie restriction and NAD+ supplementation regulate aging; and reveal the core logic of metabolic homeostasis imbalance accelerating aging.
Metabolomics and flux analysis techniques: Use liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) to analyze metabolite profiles; detect cellular oxygen consumption rate (OCR) and extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) via Seahorse XF analyzer to quantify metabolic functions.
Gene editing and model organism technologies: Construct metabolic enzyme gene knockout/knock-in cell lines and animal models (mouse, zebrafish) using CRISPR/Cas9 and RNAi; verify gene functions and metabolic pathway regulatory networks.
Single-cell metabolic analysis techniques: Combine single-cell transcriptomics and flow cytometry (fluorescent probe-labeled metabolites) to analyze metabolic heterogeneity in cell populations and track metabolic dynamics of specific cell subsets.
Bioimaging and tracing techniques: Use fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) probes, stable isotope labeling (13C, 15N), and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry imaging (MALDI-MSI) to real-time track the synthesis, transport, and distribution of metabolites.
Bioinformatics and systems metabolomics: Integrate multi-omics (genomics, transcriptomics, metabolomics) data to construct metabolic regulatory network models; predict key regulatory nodes and disease-related metabolic modules.
Related Promotional Journal Downloads

30,000+ high- quality products available online
Primary Antibodies, Secondary Antibodies, mIHC Kits, ELISA Kits, Proteins, Molecular Biology Products,Cell Lines,Reagents ...
Contact Us