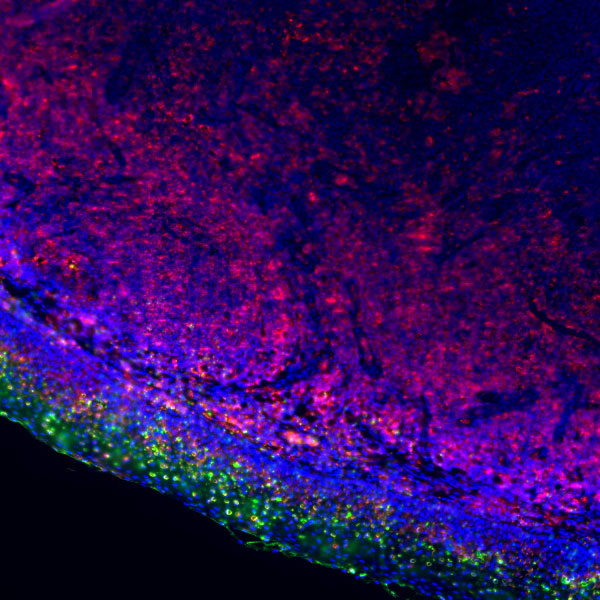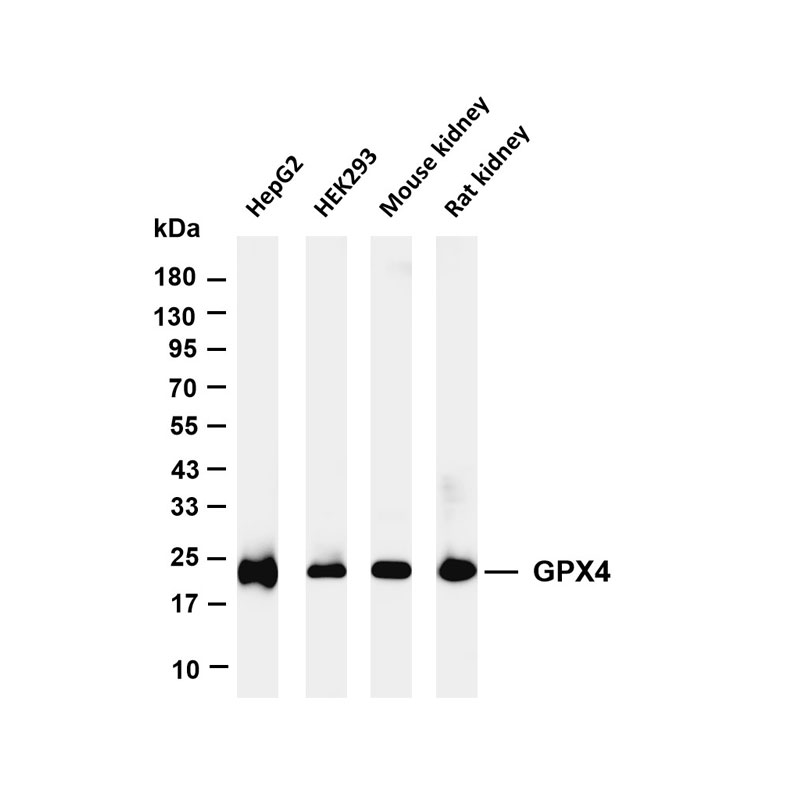
As the foundation of infectious disease research, this field aims to reveal pathogens’ molecular characteristics, mutation rules, and pathogenic basis, providing targets for diagnosis, vaccine, and drug development. Core directions include
Genomic and functional analysis: For viruses (e.g., COVID-19, influenza), bacteria (e.g., Mycobacterium tuberculosis, super drug-resistant strains), and parasites (e.g., Plasmodium, schistosomes), use whole-genome sequencing and transcriptomics to identify key virulence genes (e.g., viral spike protein genes, bacterial virulence factor genes) and their functions, and analyze pathogenic transcriptional regulatory networks in hosts. Conduct de novo genomic analysis of emerging pathogens (e.g., unknown coronaviruses, filoviruses) to quickly locate critical domains (e.g., receptor-binding domains, enzyme active sites).
Mutation and evolution rules: Track molecular evolution paths of pathogens, analyze mutation hotspots (e.g., COVID-19 S protein mutations, influenza antigenic drift) via phylogenetic trees, and reveal mutations’ impacts on transmissibility (e.g., airborne efficiency), pathogenicity (e.g., severe rate), and immune escape (e.g., evading vaccine-induced antibodies). Study drug resistance evolution mechanisms (e.g., bacterial β-lactamase genes, Candida albicans ERG11 mutations) to clarify molecular mechanisms (e.g., horizontal gene transfer, spontaneous mutation selection) and predict epidemic trends of drug-resistant strains.
Pathogenic mechanism analysis: Elucidate key steps of pathogen invasion (e.g., viral surface proteins binding host receptors like COVID-19 S protein to ACE2, bacteria injecting virulence factors via secretion systems like Type III secretion system). Study pathogen-induced host cell metabolic reprogramming (e.g., M. tuberculosis regulating host lipid metabolism for nutrition, Plasmodium disrupting erythrocyte oxidative stress balance to cause hemolysis) and identify key molecular targets.
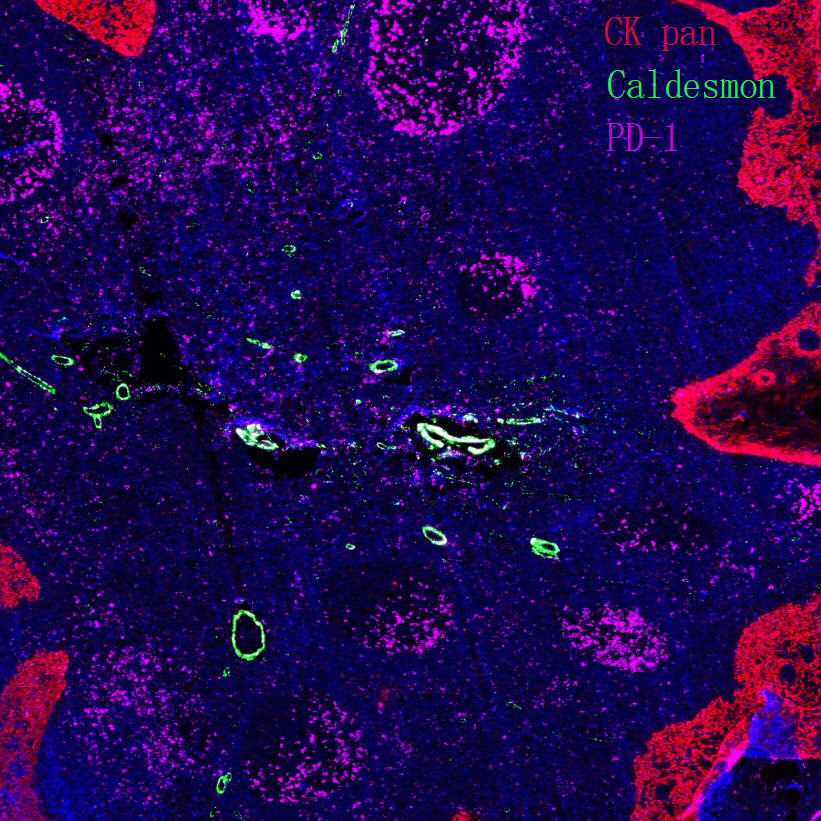
Focusing on host-pathogen "offense-defense interactions", this field deciphers how the immune system recognizes and eliminates pathogens, as well as pathogens’ immune escape strategies, providing a basis for immunotherapy and vaccine design:
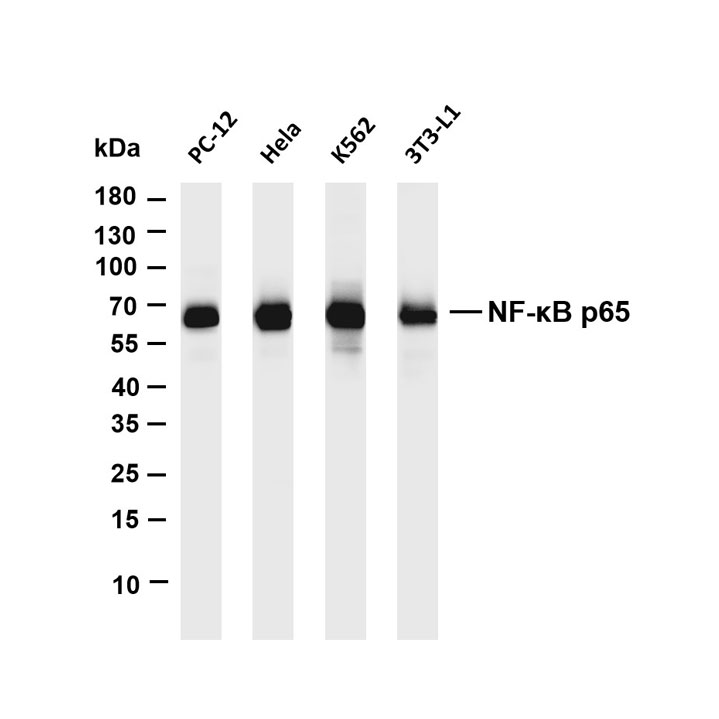
Innate immune recognition and activation: Investigate how host pattern recognition receptors (PRRs, e.g., TLR, RIG-I) recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs, e.g., viral RNA, bacterial lipopolysaccharide), activate downstream signaling pathways (e.g., NF-κB, IRF), induce interferons and cytokines, and initiate early immune defense. Analyze functional regulation of innate immune cells (e.g., macrophages, dendritic cells, NK cells) and how pathogens inhibit their activity (e.g., viral proteins blocking interferon signals).
Adaptive immune response regulation: Reveal activation and differentiation mechanisms of T/B cells (e.g., CD4+ T cells differentiating into Th1/Th2/Treg subsets, B cells producing high-affinity antibodies via somatic hypermutation, and memory B cell formation determining long-term vaccine protection). Study immune memory maintenance mechanisms in chronic infections (e.g., AIDS, viral hepatitis) and ways to enhance memory immune responses by regulating the immune microenvironment (e.g., follicular helper T cell function).
Immune escape and immunopathology: Decipher pathogen immune escape strategies (e.g., influenza evading antibody recognition via antigenic drift, HBV persisting via host genome integration, HPV inhibiting host cell apoptosis). Study immunopathological mechanisms (e.g., COVID-19-induced cytokine storm, tuberculosis granuloma formation) to clarify how excessive immune responses cause tissue damage, providing a theoretical basis for immunomodulators (e.g., cytokine inhibitors).
From a macro-micro integrated perspective, this field analyzes transmission paths and influencing factors of infectious diseases in populations and environments, providing a scientific basis for prevention and control strategies:
Transmission routes and vector mechanisms: Study vector-borne transmission (e.g., mosquitoes carrying pathogens via salivary glands for dengue/malaria, ticks transmitting pathogens during blood-sucking for Lyme disease) and the impact of vector drug resistance on transmission efficiency. Clarify key conditions for contact/airborne transmission (e.g., COVID-19 survival time in aerosols related to temperature/humidity, norovirus transmission threshold via food/water contamination).
Host susceptibility factors: Explore molecular bases of population susceptibility (e.g., CCR5Δ32 mutation conferring AIDS resistance, age-related immune decline increasing influenza susceptibility in the elderly, underlying diseases like diabetes raising severe COVID-19 risk). Study the regulatory role of the host microbiome (e.g., gut microbiota regulating immune function via metabolites like short-chain fatty acids) and how antibiotic-induced dysbiosis increases infection risk.
Ecological and environmental regulation: Analyze the impact of climate change on infectious disease epidemics (e.g., global warming expanding mosquito habitats and dengue/malaria endemic areas, extreme weather like floods increasing waterborne diseases such as cholera). Study the impact of human activities (e.g., cross-border trade and population movement accelerating transregional pathogen spread, antibiotic abuse in aquaculture accumulating environmental drug-resistant genes).
Related Promotional Journal Downloads

30,000+ high- quality products available online
Primary Antibodies, Secondary Antibodies, mIHC Kits, ELISA Kits, Proteins, Molecular Biology Products,Cell Lines,Reagents ...
Contact Us