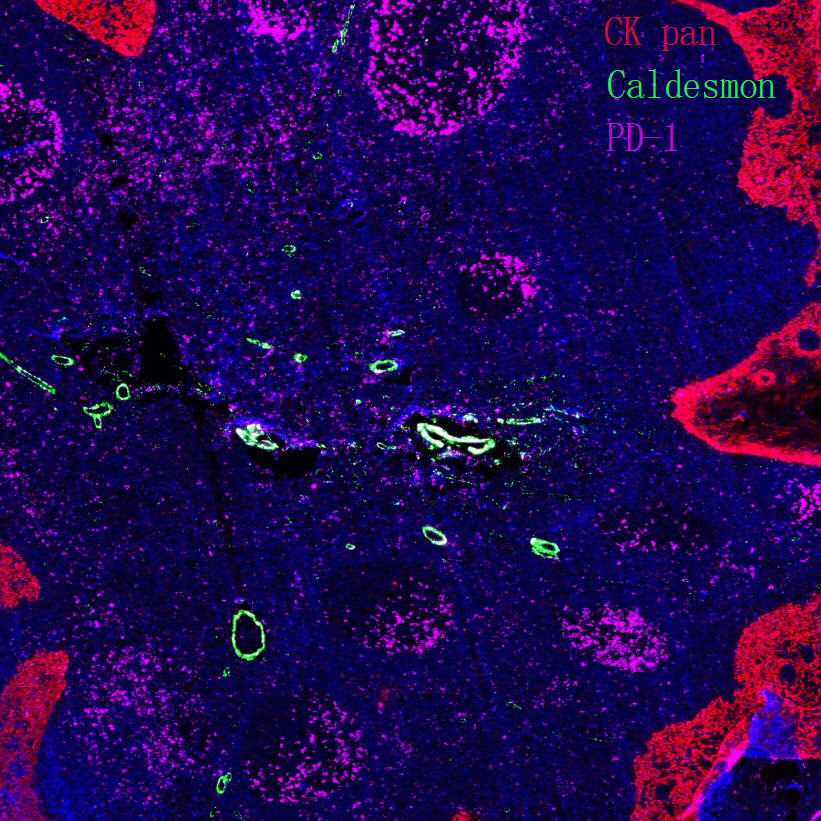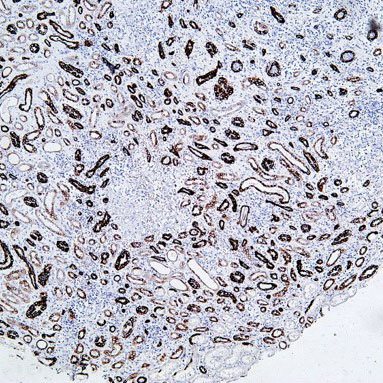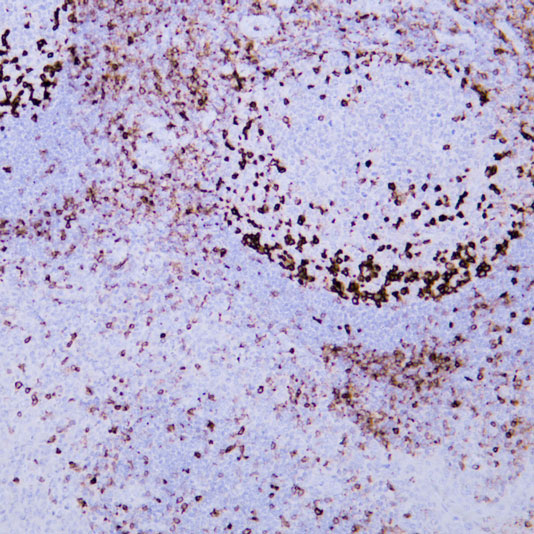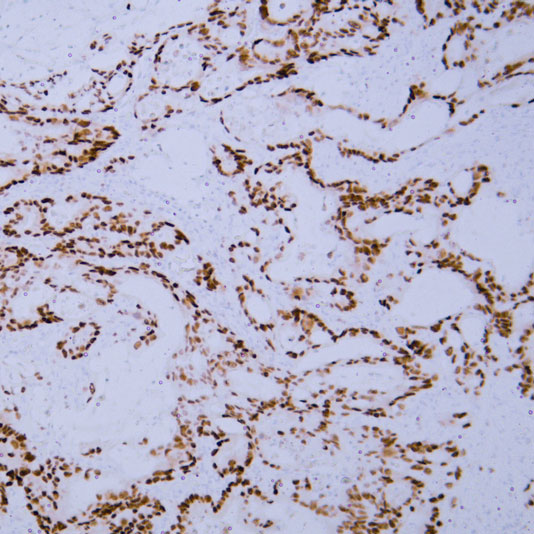
Basic research in developmental biology focuses on the "ordered construction of life from zygote to mature organism". Its core is to decipher the molecular regulatory networks of cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and tissue/organ formation, as well as to reveal the underlying logic of maintaining developmental homeostasis and pathogenesis of developmental abnormalities.
1. Molecular Regulatory Mechanisms of Embryonic Development
Early embryonic pattern formation: Explore how zygotes establish body axes (anterior-posterior axis, dorsal-ventral axis) through asymmetric division, how key signaling pathways (e.g., Wnt, BMP, Hedgehog) regulate cell fate determination, and the regulatory role of homeobox genes (Hox genes) in somite differentiation and organ localization.
Cell differentiation and lineage establishment: Decipher the molecular switches that direct the differentiation of pluripotent stem cells (e.g., embryonic stem cells, adult stem cells) into various tissue cells (neurons, muscle cells, hematopoietic cells, etc.), with a focus on the regulatory functions of epigenetic modifications (DNA methylation, histone modification) and non-coding RNAs.
Organogenesis and morphogenesis: Study the formation process of vital organs such as the heart, kidneys, and nervous system, clarify the coordinated mechanisms of cell migration, proliferation, and polarity establishment, and the signaling role of "organizer" cells (e.g., Spemann-Mangold organizer) in organ development.
2.Stem Cells and Regenerative Development
Balance between stem cell self-renewal and differentiation: Reveal the molecular network maintaining stem cell pluripotency (e.g., core transcription factors like Oct4, Sox2, Nanog) and the regulatory mechanism of the niche on stem cell fate.
Developmental recapitulation in tissue regeneration: Investigate the molecular basis of limb regeneration in lower organisms (e.g., salamanders) and heart regeneration in zebrafish, analyze the regulatory logic of cell dedifferentiation and redifferentiation during regeneration, providing theoretical references for human tissue repair.
Plasticity of adult stem cells: Study the activation mechanism of adult stem cells in injury repair and the possibility of translineage differentiation, exploring the application potential of stem cells in regenerative medicine.
3.Developmental Homeostasis and Abnormal Regulation
Precise control of developmental timing: Decipher how biological clocks and signal gradient concentrations regulate the timing of developmental processes to avoid premature or delayed organ development.
Association between developmental abnormalities and diseases: Explore the molecular etiology of congenital malformations (e.g., spina bifida, congenital heart disease), analyze the impact of development-related genetic variations (e.g., copy number variations, point mutations) on embryonic development; reveal the association between abnormal developmental mechanisms and adult diseases (e.g., tumors, neurodegenerative diseases), such as abnormal activation of development-related signaling pathways leading to tumorigenesis.
Developmental regulation by environmental factors: Study the impact of environmental factors (e.g., nutritional status, chemical toxins, microbiome) on embryonic development, and decipher the role of epigenetic modifications in "developmental programming" (e.g., intrauterine malnutrition increasing susceptibility to metabolic diseases in adulthood).
4. Evolutionary Developmental Biology (Evo-Devo)
Evolutionary conservation of key developmental genes: Compare the sequence and functional differences of core developmental genes (e.g., Hox gene family, Wnt pathway genes) across different species (from invertebrates to vertebrates), revealing the conservation and innovation of developmental mechanisms in evolution.
Developmental basis of morphological evolution: Decipher the developmental regulatory mechanisms underlying the formation of species-specific traits (e.g., bird feathers, mammalian placenta), and explore how variations in developmental genes drive morphological evolution.
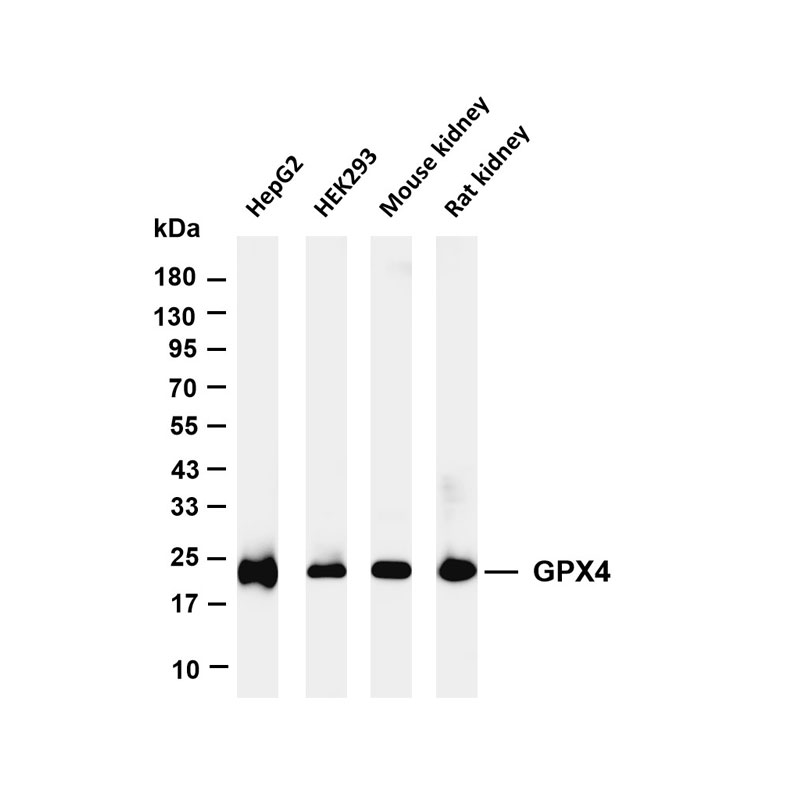
Model organism systems: Rely on classic model organisms such as Drosophila, zebrafish, mice, and Caenorhabditis elegans, combined with gene editing (CRISPR/Cas9) and transgenic technologies to construct mutants for gene function analysis.
Single-cell omics technologies: Map cell lineage atlases during embryonic development and precisely locate molecular characteristics of different cell types through single-cell transcriptome and single-cell epigenome sequencing.
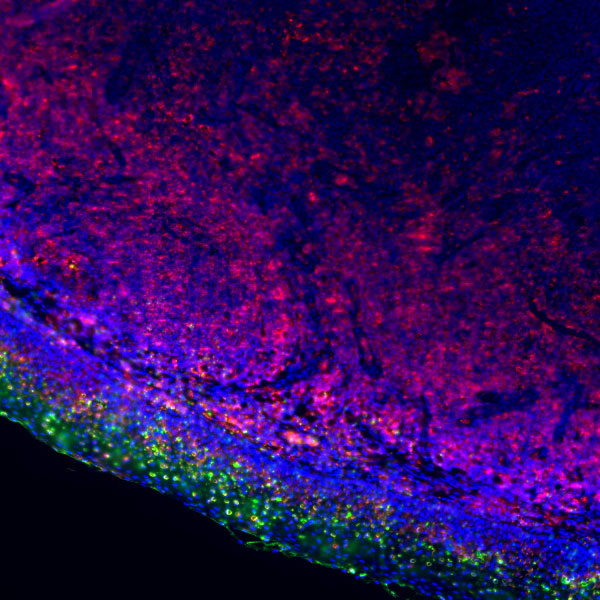
In vivo imaging technologies: Use fluorescence labeling, confocal microscopy, light-sheet microscopy, etc., to track the dynamics of cell migration, division, and differentiation during embryonic development in real time.
Bioinformatics and systems biology: Integrate multi-omics data to construct molecular network models of developmental regulation and predict key regulatory nodes.
Related Promotional Journal Downloads

30,000+ high- quality products available online
Primary Antibodies, Secondary Antibodies, mIHC Kits, ELISA Kits, Proteins, Molecular Biology Products,Cell Lines,Reagents ...
Contact Us