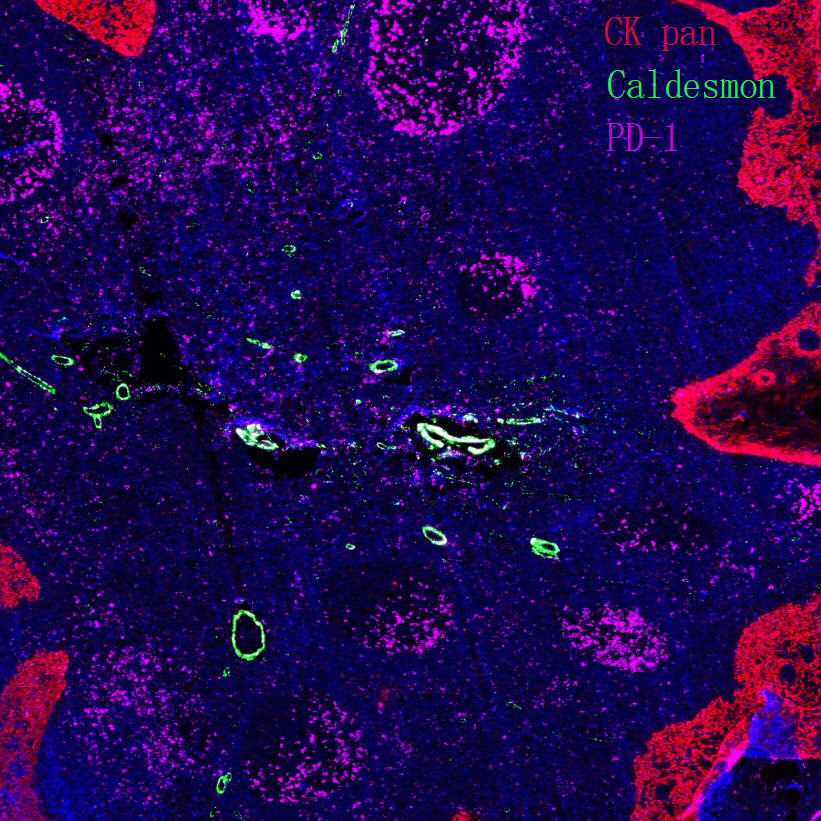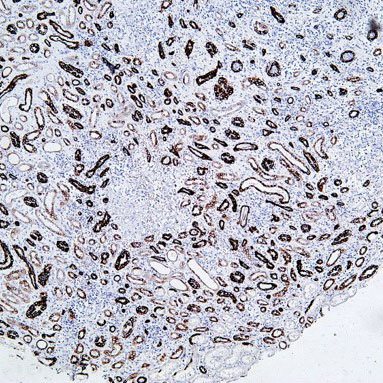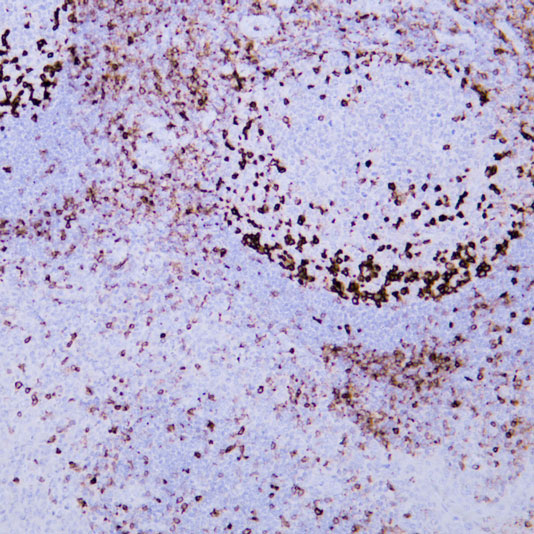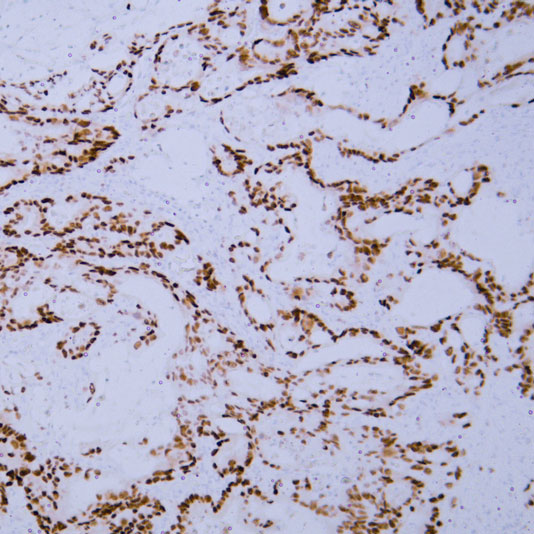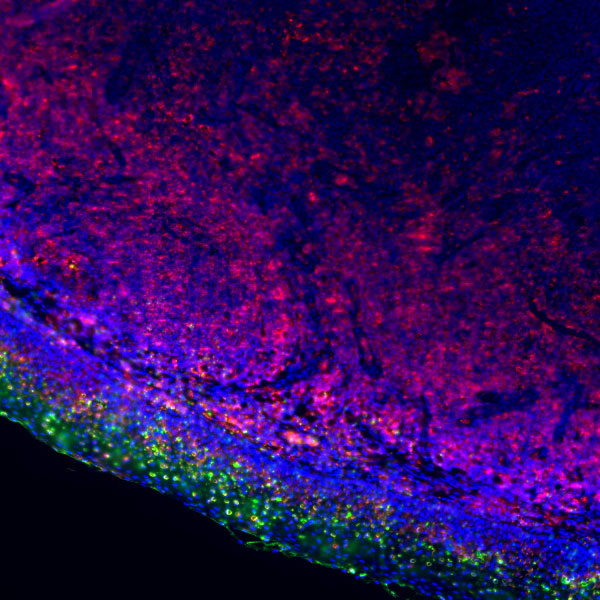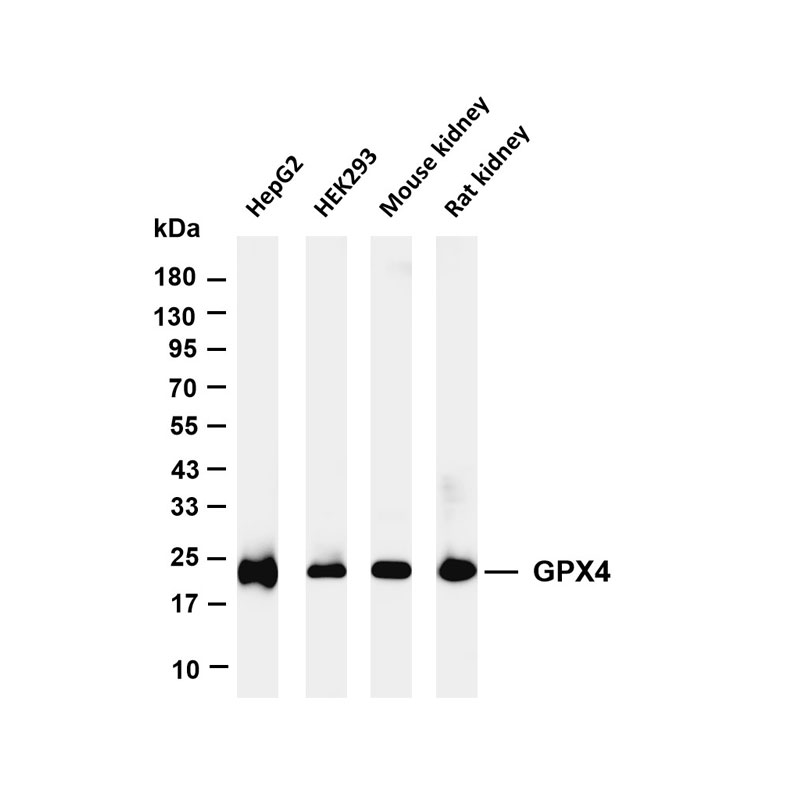
Epigenetics is a key field that regulates gene expression without altering DNA sequences, serving as a core frontier in current life science research.
Focus on factors such as histone modification and DNA methylation, investigating their impacts on gene expression, cell development, and differentiation.
Histone Modification Biomarkers
Methylation Modifications: H3K4me3, H3K27me3, H3K36me3, H3K9me3
Acetylation Modifications: H3K27ac, H3K9ac, H4K16ac
Phosphorylation Modifications: H3S10ph, H2AXS139ph (γ-H2AX)
DNA Methylation Biomarkers
Global Methylation: 5-Methylcytosine (5-mC), 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC)
Site-Specific Methylation: CpG island methylation in promoter regions (e.g., p16, RASSF1A gene promoters)
Regulatory Enzymes: DNMT1, DNMT3A, DNMT3B, TET1, TET2, TET3
Decode the molecular pathways through which histone modification, DNA methylation, and other epigenetic factors regulate gene transcription and silencing. Clarify their roles in cellular physiological processes such as proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis, as well as their response mechanisms to environmental signals.
Histone Modification Regulatory Biomarkers
Activating Modifications: H3K4me3 (gene transcription activation), H3K27ac (enhancer activation)
Repressive Modifications: H3K27me3 (gene silencing), H3K9me3 (heterochromatin formation)
Regulatory Enzymes: EZH2 (H3K27 methyltransferase), p300/CBP (acetyltransferase), HDAC1/2 (deacetylase)
DNA Methylation Regulatory Biomarkers
Modified Products: 5-mC (methylation marker), 5-hmC (demethylation intermediate)
Key Enzymes: DNMT3A/3B (de novo methyltransferase), TET1/2 (demethylase)
Target Sites: CpG island methylation in tumor suppressor gene promoters (e.g., BRCA1, PTEN)
Non-Coding RNA Regulatory Biomarkers
MicroRNA (miRNA): let-7 family, miR-155 (regulate gene expression)
Long Non-Coding RNA (lncRNA): XIST (X-chromosome inactivation), HOTAIR (gene silencing regulation)
Focus on the mechanisms by which abnormal epigenetic modifications (e.g., DNA methylation disorders, histone modification imbalances, abnormal non-coding RNA regulation) contribute to the occurrence and development of major diseases such as tumors and neurological disorders. Reveal their core value as disease-causing factors or therapeutic targets, providing theoretical support for early diagnosis, targeted therapy, and prognostic evaluation of diseases.
Tumor-Related Epigenetic Biomarkers
Abnormal DNA Methylation: Hypermethylation of tumor suppressor gene promoters (p16, RASSF1A, MGMT), hypomethylation of proto-oncogenes; decreased 5-hmC levels (e.g., liver cancer, lung cancer)
Abnormal Histone Modifications: Abnormally elevated H3K27me3 (lymphoma, glioma), downregulated H3K4me3 (breast cancer, colorectal cancer), overexpression of EZH2 (multiple malignant tumors)
Abnormal Non-Coding RNAs: Overexpression of miR-155, miR-21 (lung cancer, gastric cancer), high expression of lncRNA HOTAIR (related to breast cancer metastasis), abnormal upregulation of lncRNA MALAT1 (lung cancer, liver cancer)
Neurological Disorder-Related Epigenetic Biomarkers
Abnormal DNA Methylation: Hypomethylation of APP gene promoter (Alzheimer's disease), hypermethylation of BDNF gene promoter (depression, schizophrenia)
Abnormal Histone Modifications: Decreased H3K9ac levels (Alzheimer's disease), abnormal H3K4me3 expression (Parkinson's disease), overexpression of HDAC6 (dopaminergic neuron damage in Parkinson's disease)
Abnormal Non-Coding RNAs: Overexpression of miR-134 (epilepsy), downregulated miR-124 (schizophrenia), high expression of lncRNA BACE1-AS (Alzheimer's disease)
Related Promotional Journal Downloads

30,000+ high- quality products available online
Primary Antibodies, Secondary Antibodies, mIHC Kits, ELISA Kits, Proteins, Molecular Biology Products,Cell Lines,Reagents ...
Contact Us