- Home
- Products
- Pathway
- Support
- Contact Us

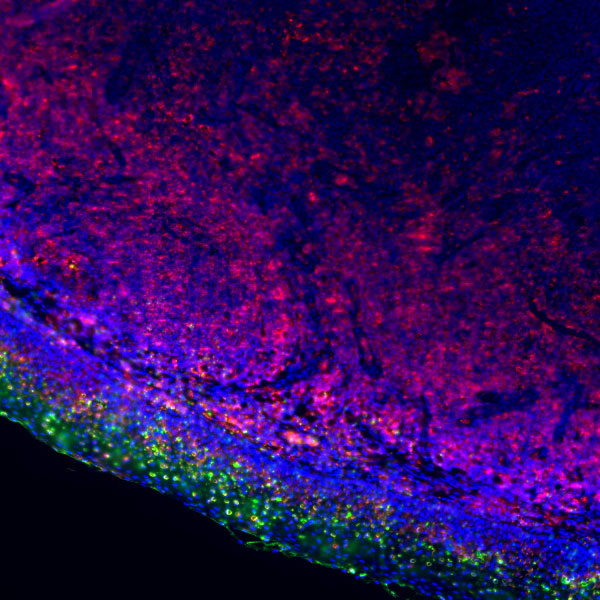
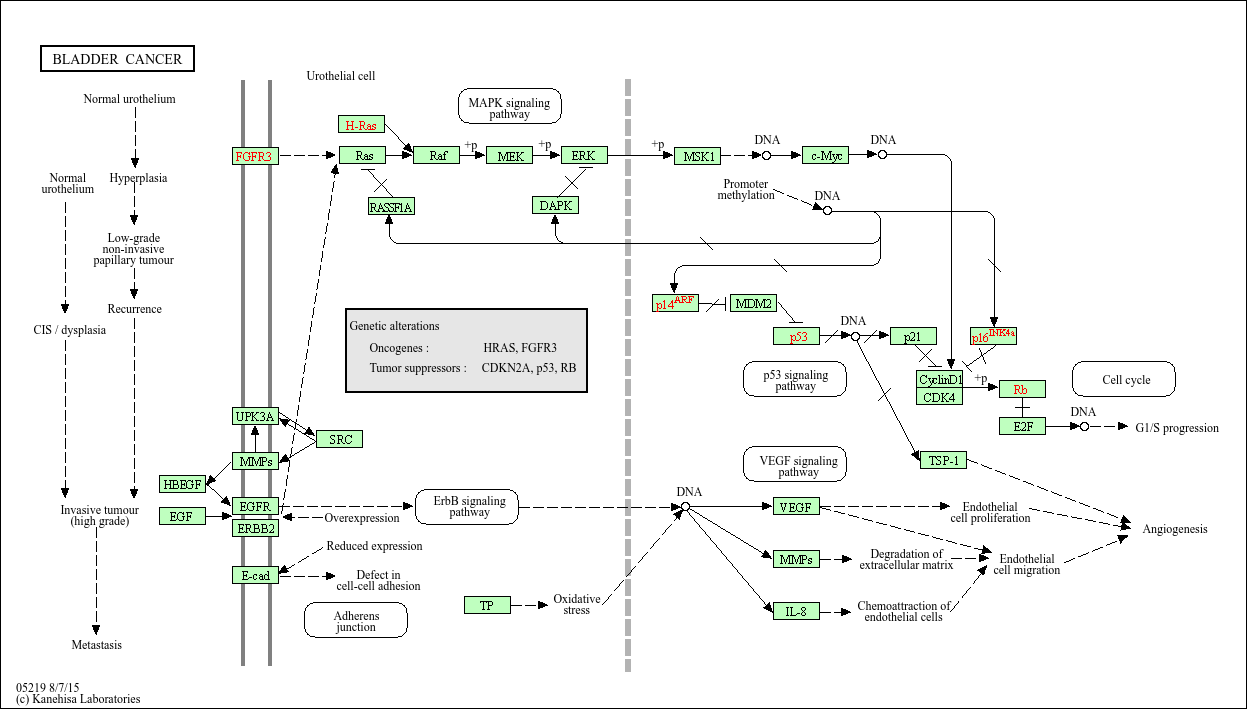
Bladder cancer
Core of basic research: Explore the synergistic effects of proto-oncogene activation (FGFR3, PI3K) and tumor suppressor gene inactivation (TP53, RB1), as well as the carcinogenic mechanisms driven by risk factors such as smoking and chronic inflammation on bladder mucosal epithelial cells. Focus on the molecular subtype differences between non-muscle-invasive and muscle-invasive tumors.
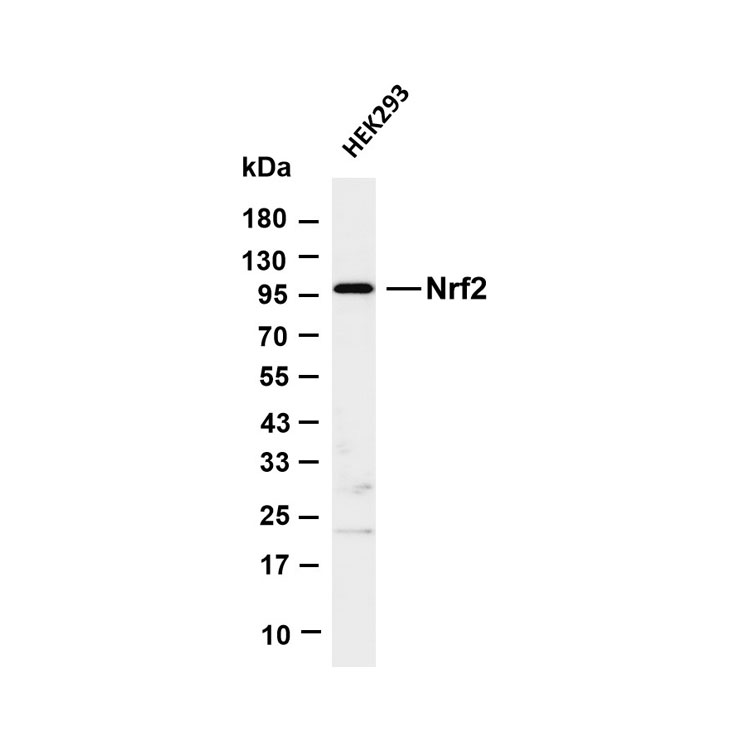
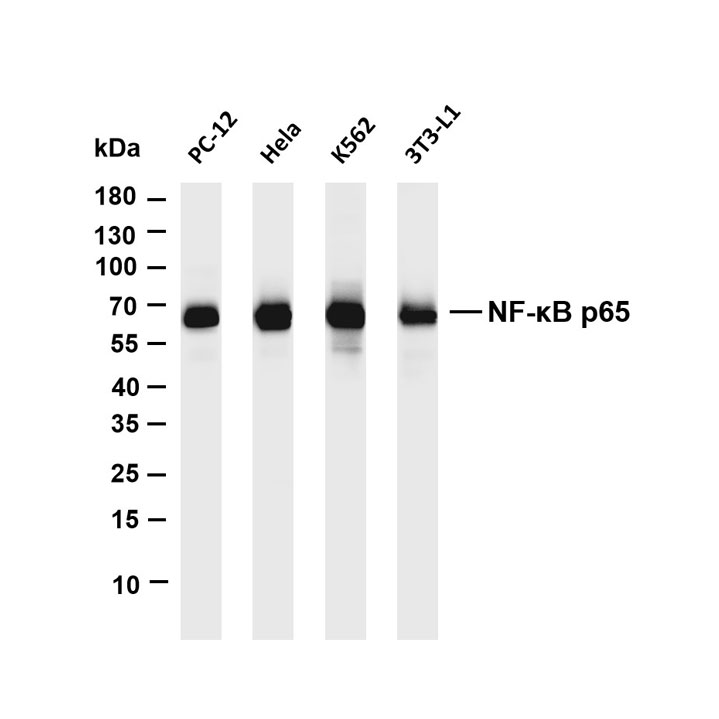
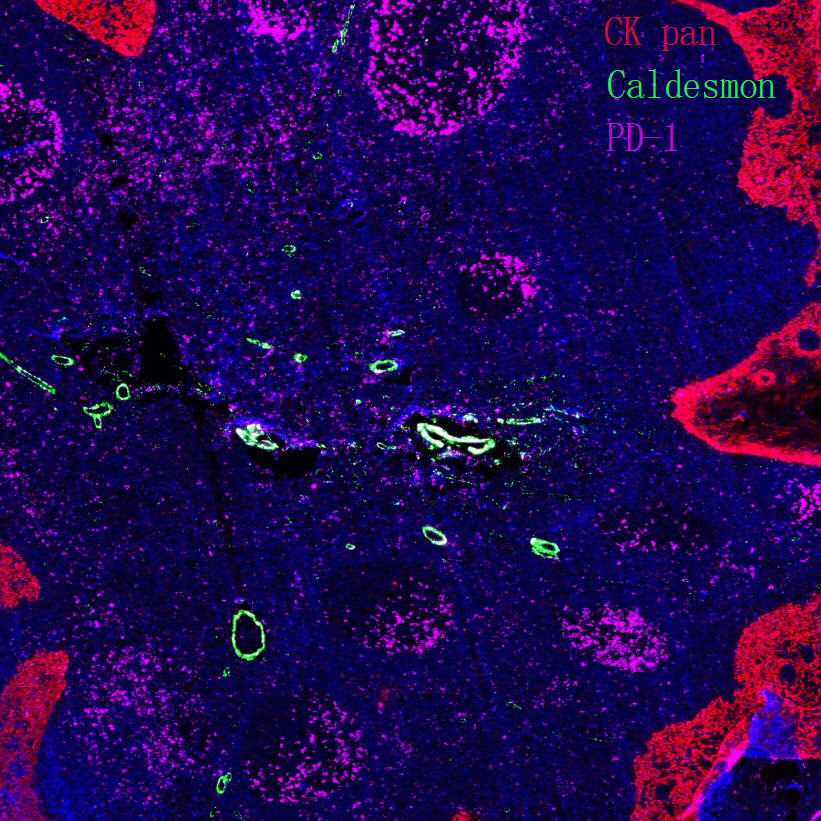
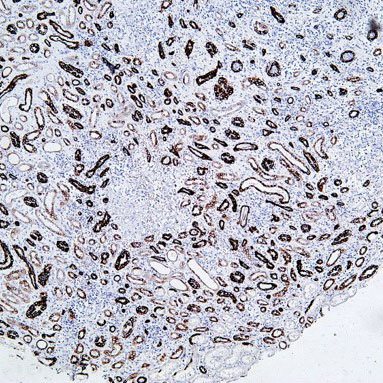
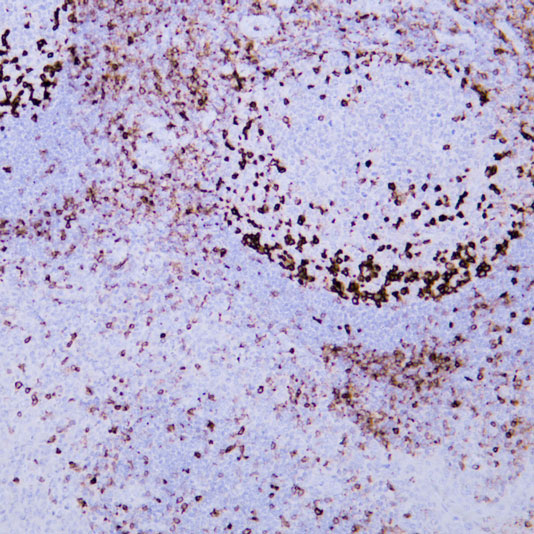
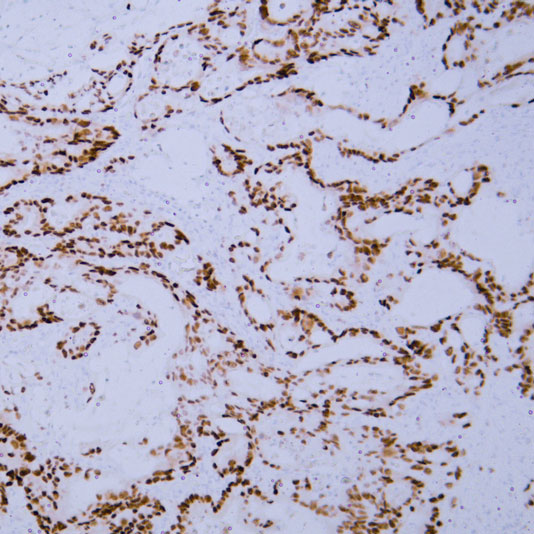
Core key proteins: FGFR3 (receptor tyrosine kinase, promotes proliferation upon mutation), PI3K/Akt (core of signaling pathway, activation enhances cell survival), TP53 (tumor suppressor gene, loss of apoptotic regulation upon inactivation), RB1 (cell cycle regulator, inactivation causes cycle disorders), Nectin-2 (cell adhesion molecule involved in invasion), PD-L1 (immune checkpoint molecule mediating immune escape).
Core key proteins: FGFR3 (receptor tyrosine kinase, promotes proliferation upon mutation), PI3K/Akt (core of signaling pathway, activation enhances cell survival), TP53 (tumor suppressor gene, loss of apoptotic regulation upon inactivation), RB1 (cell cycle regulator, inactivation causes cycle disorders), Nectin-2 (cell adhesion molecule involved in invasion), PD-L1 (immune checkpoint molecule mediating immune escape).
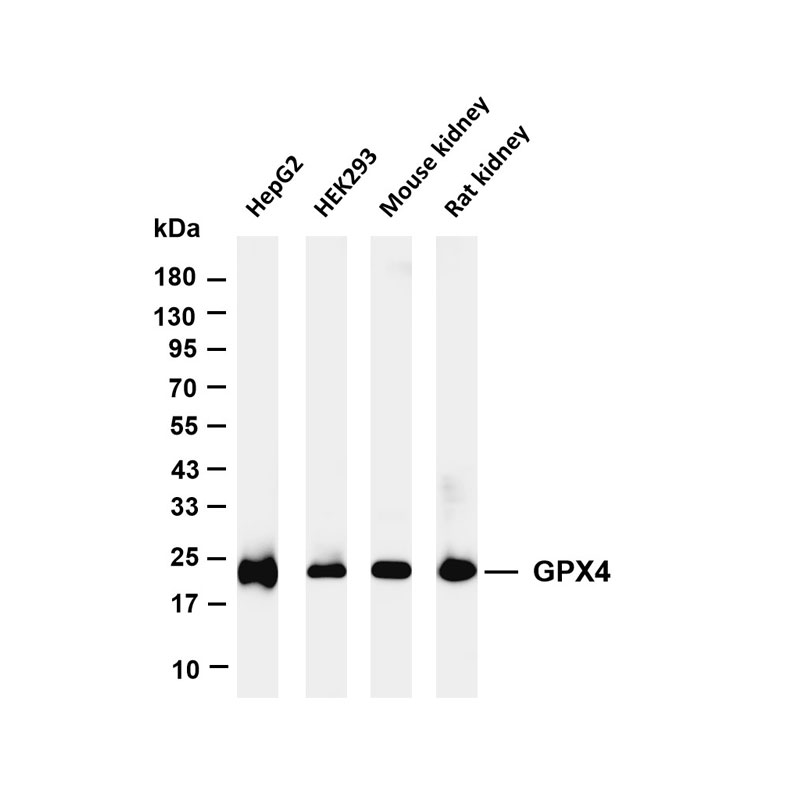
Product list
-
{{item.title}}{{item.react}}{{item.applicat}}
Product list
Product name
Reactivity
Application
Related Resource Links
Related Promotional Journal Downloads

Explore Our Recommended Popular Products
More products
30,000+ high- quality products available online
Primary Antibodies, Secondary Antibodies, mIHC Kits, ELISA Kits, Proteins, Molecular Biology Products,Cell Lines,Reagents ...
Contact Us