- Home
- Products
- Pathway
- Support
- Contact Us

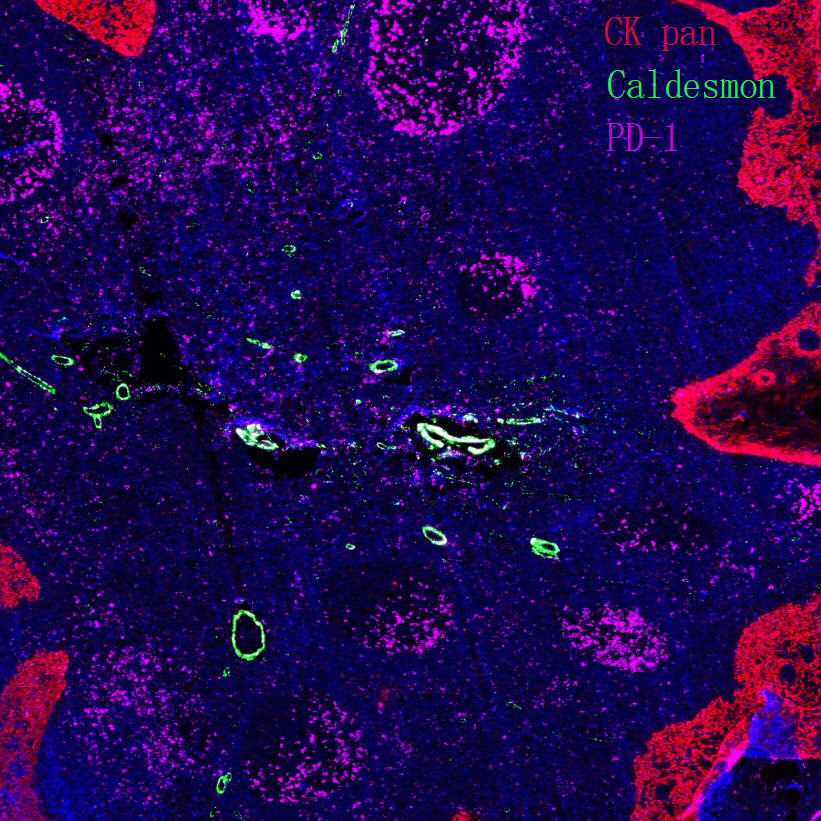
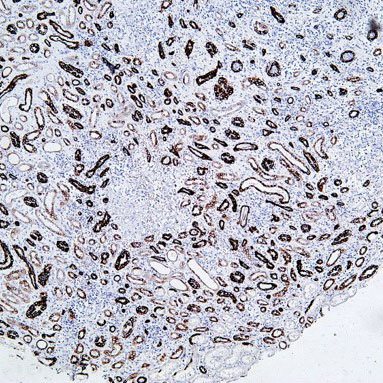
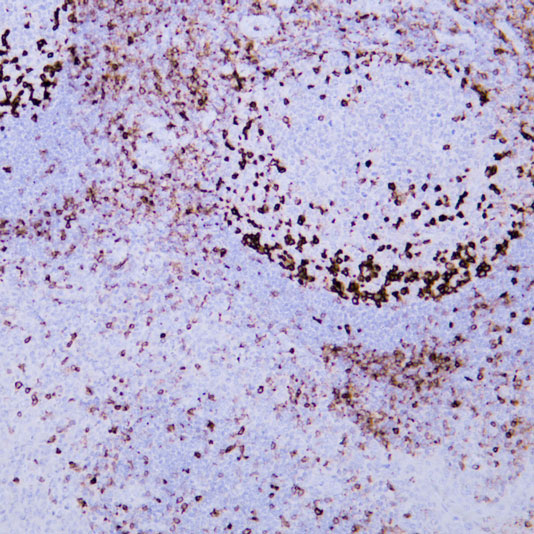
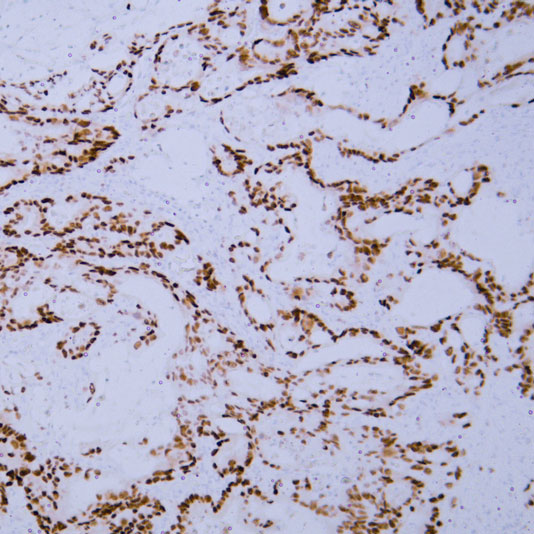
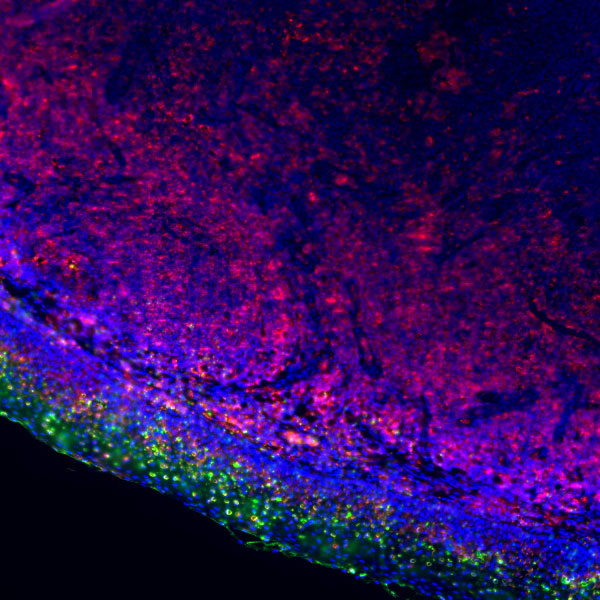
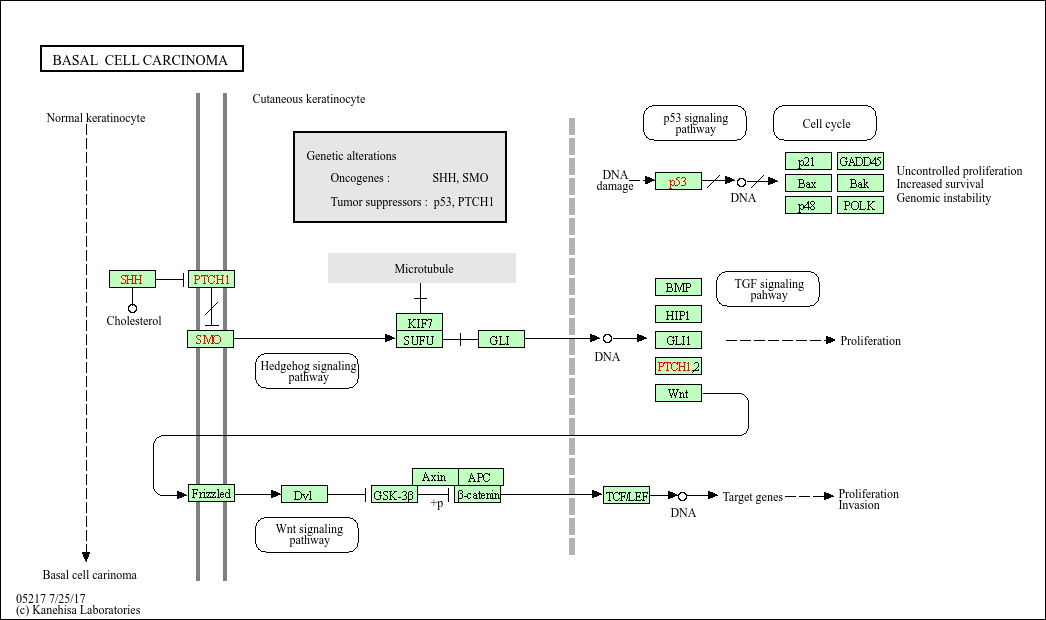
Basal cell carcinoma
Core of basic research: Centered on the abnormal activation of the Hedgehog signaling pathway, focusing on deciphering ultraviolet-induced mutations in pathway molecules (e.g., PTCH1 inactivation, SMO activation) and the impact of downstream transcriptional regulatory networks on the proliferation of cutaneous basal cells. This serves as the foundation for the development of Smo-targeted inhibitors.
Core key proteins: PTCH1 (pathway inhibitor, inactivated by mutation), SMO (pathway activator, abnormally activated), Gli1/2 (downstream transcription factors regulating proliferation-related genes), SUFU (Gli inhibitor with functional abnormalities), TP53 (DNA damage repair, mutation increases cancer risk), NOTCH1 (assists in regulating cell fate).
Core key proteins: PTCH1 (pathway inhibitor, inactivated by mutation), SMO (pathway activator, abnormally activated), Gli1/2 (downstream transcription factors regulating proliferation-related genes), SUFU (Gli inhibitor with functional abnormalities), TP53 (DNA damage repair, mutation increases cancer risk), NOTCH1 (assists in regulating cell fate).
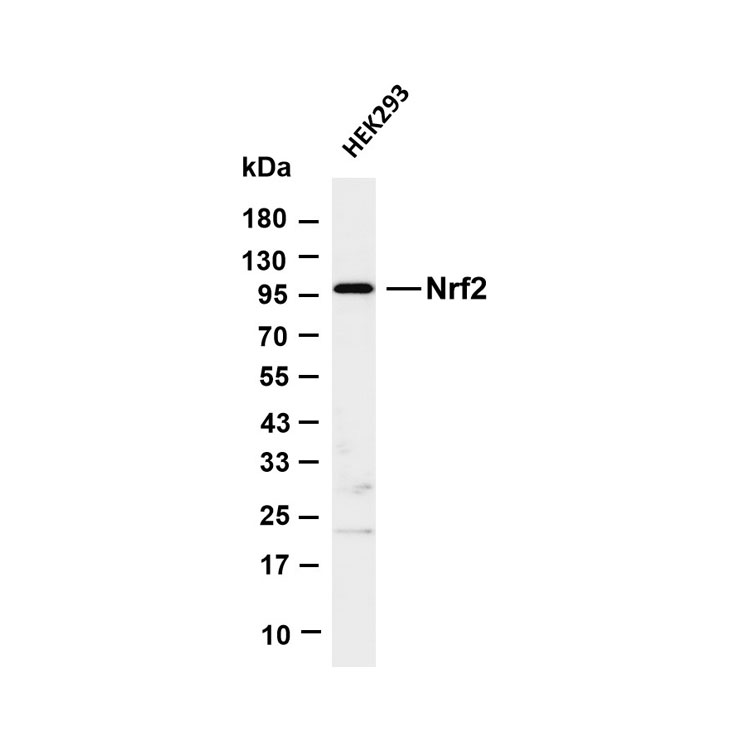
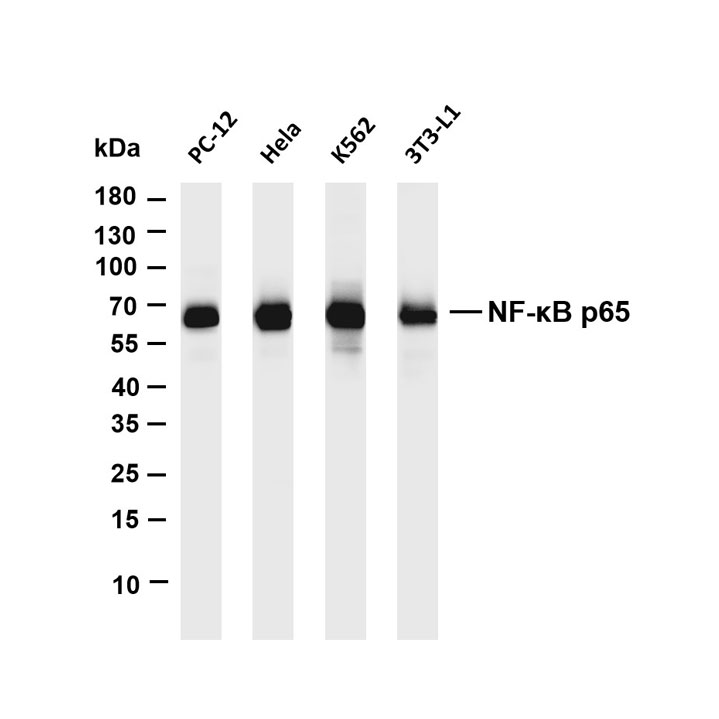
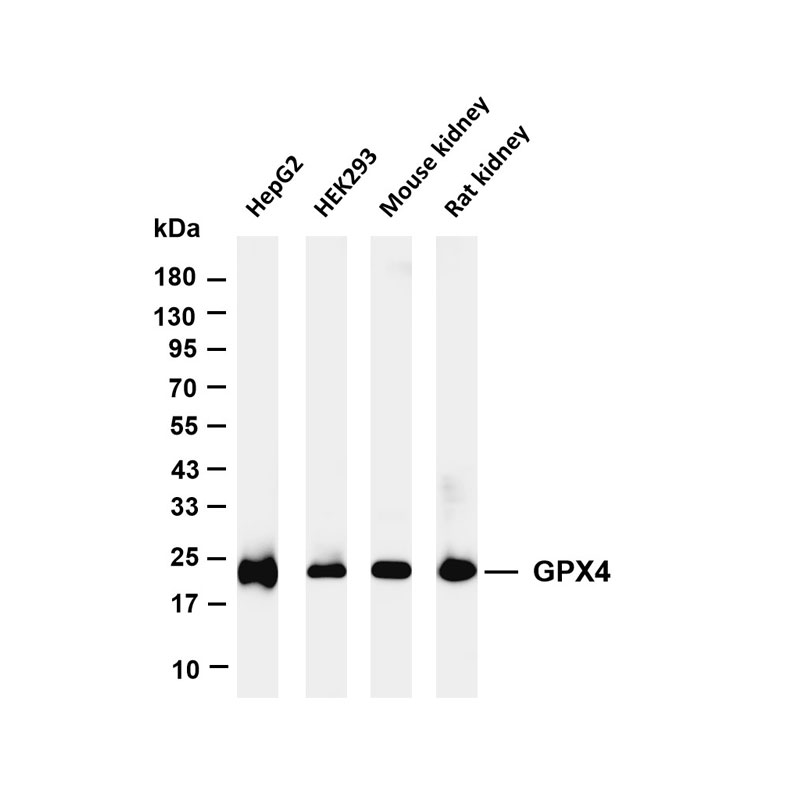
Product list
-
{{item.title}}{{item.react}}{{item.applicat}}
Product list
Product name
Reactivity
Application
Related Resource Links
Related Promotional Journal Downloads

Explore Our Recommended Popular Products
More products
30,000+ high- quality products available online
Primary Antibodies, Secondary Antibodies, mIHC Kits, ELISA Kits, Proteins, Molecular Biology Products,Cell Lines,Reagents ...
Contact Us