- Home
- Products
- Pathway
- Support
- Contact Us

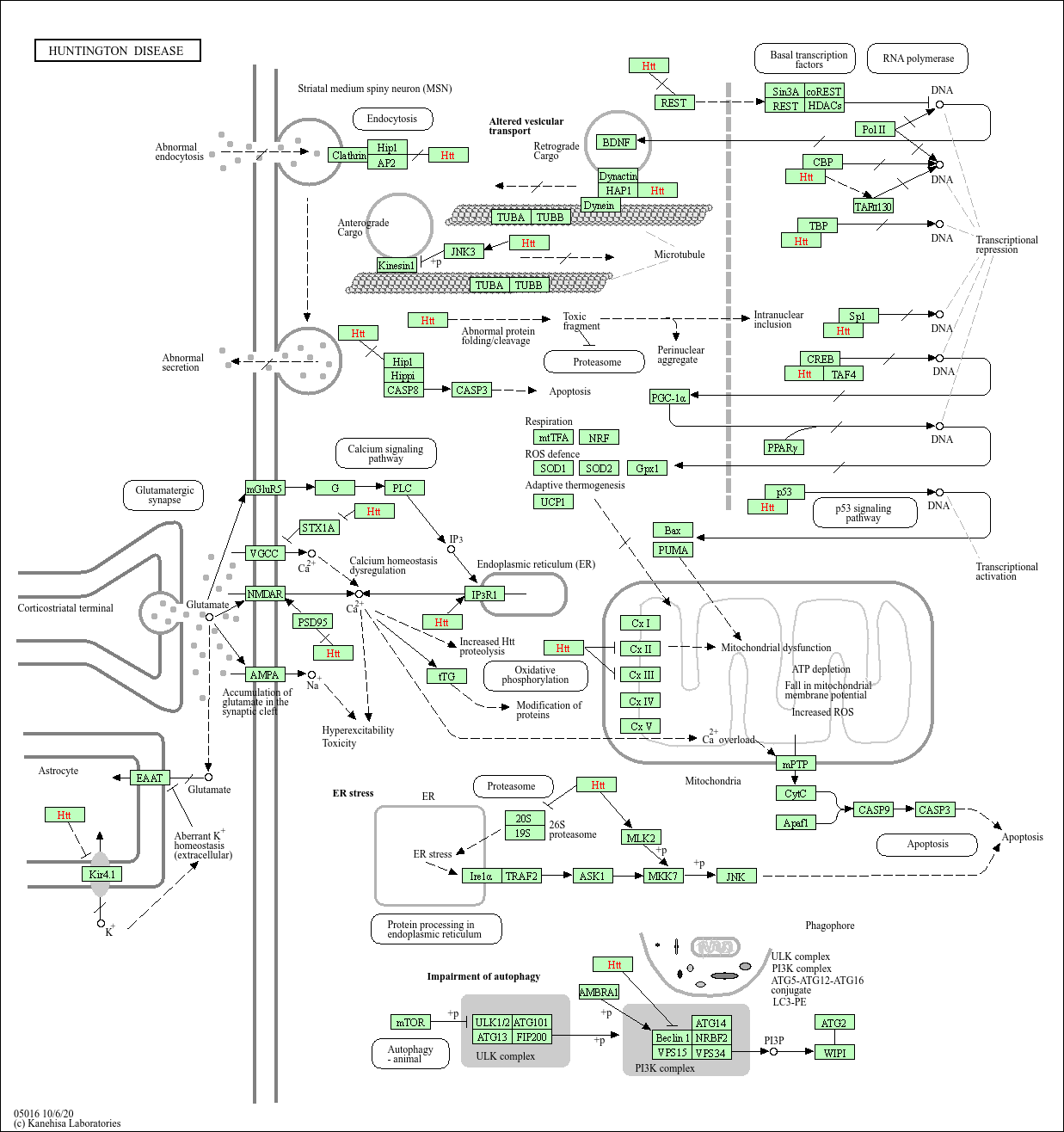
Huntington disease
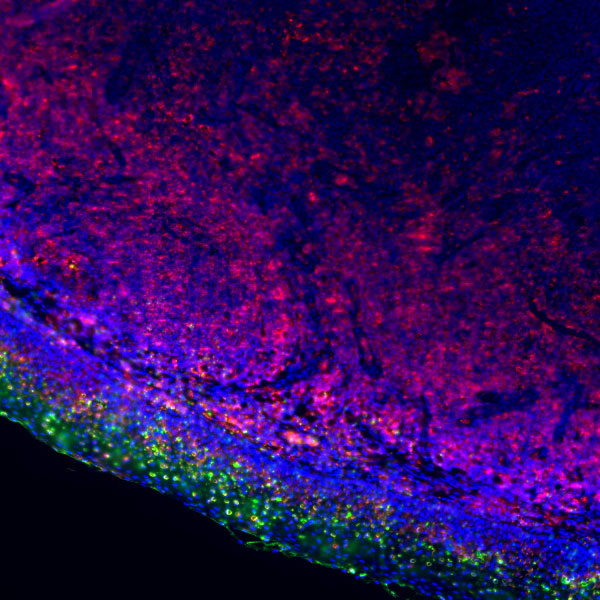
Core of basic research: Focus on the abnormal aggregation of mHTT protein caused by CAG repeat expansion in the HTT gene, explore its toxic mechanisms on basal ganglia neurons (e.g., inhibiting transcription, interfering with mitochondrial function), as well as the expression regulation of neurotrophic factors such as BDNF.
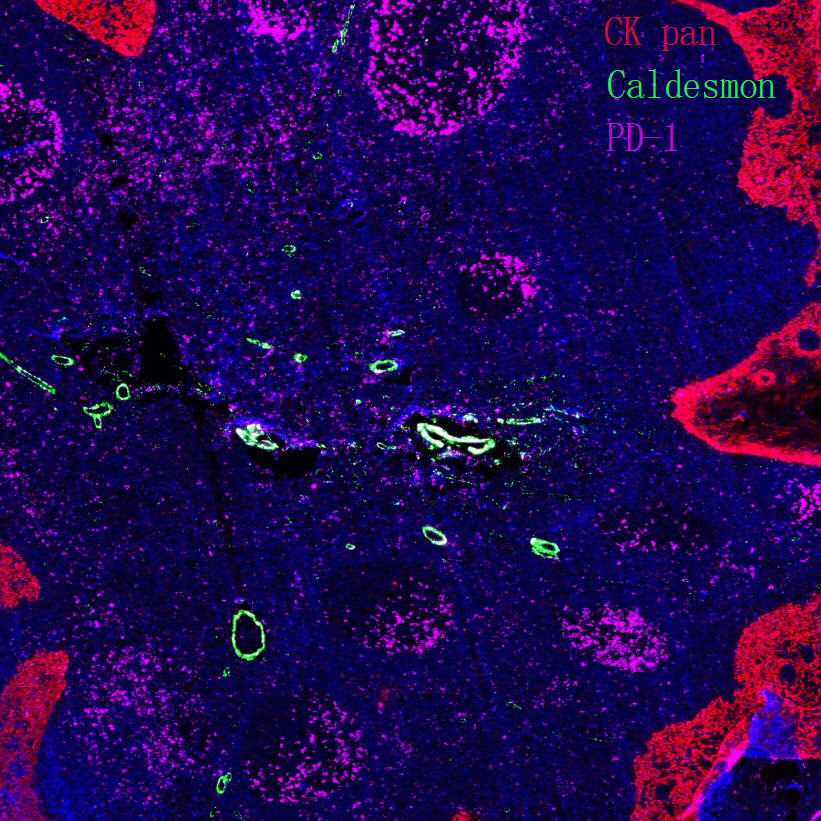
Core key proteins: mHTT (mutant huntingtin protein producing toxicity upon abnormal aggregation), HAP1 (binds to mHTT affecting cellular transport), p53 (mediates mHTT-induced apoptosis), CASP3 (caspase 3 executing apoptosis), BDNF (brain-derived neurotrophic factor, decreased expression causes neuronal damage), NMDA receptor (excessive activation exacerbates neuronal damage).
Core key proteins: mHTT (mutant huntingtin protein producing toxicity upon abnormal aggregation), HAP1 (binds to mHTT affecting cellular transport), p53 (mediates mHTT-induced apoptosis), CASP3 (caspase 3 executing apoptosis), BDNF (brain-derived neurotrophic factor, decreased expression causes neuronal damage), NMDA receptor (excessive activation exacerbates neuronal damage).
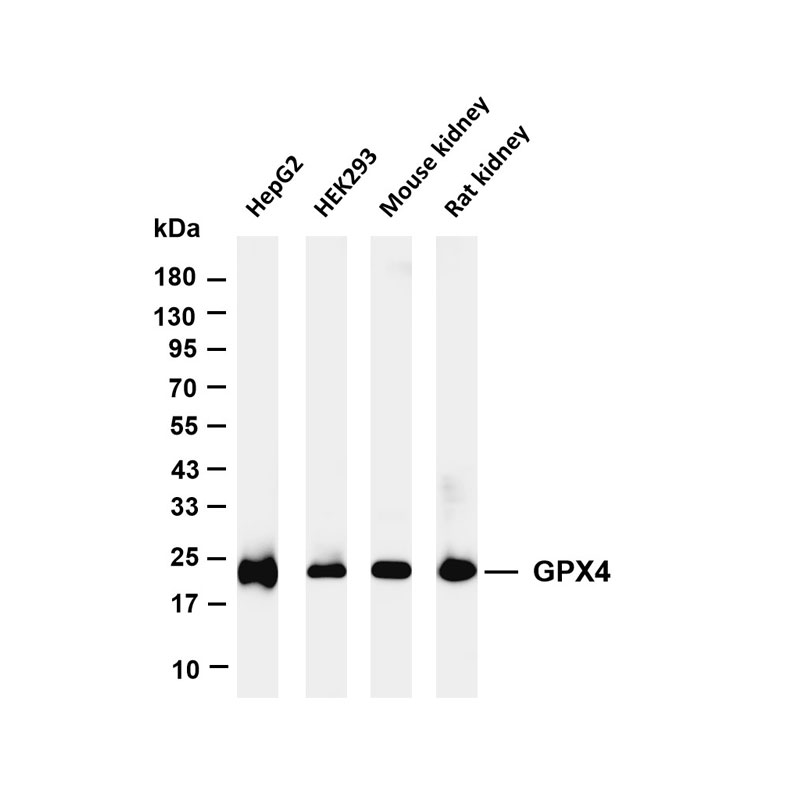
Product list
-
{{item.title}}{{item.react}}{{item.applicat}}
Product list
Product name
Reactivity
Application
Related Resource Links
Related Promotional Journal Downloads

Explore Our Recommended Popular Products
More products
30,000+ high- quality products available online
Primary Antibodies, Secondary Antibodies, mIHC Kits, ELISA Kits, Proteins, Molecular Biology Products,Cell Lines,Reagents ...
Contact Us