- Home
- Products
- Pathway
- Support
- Contact Us

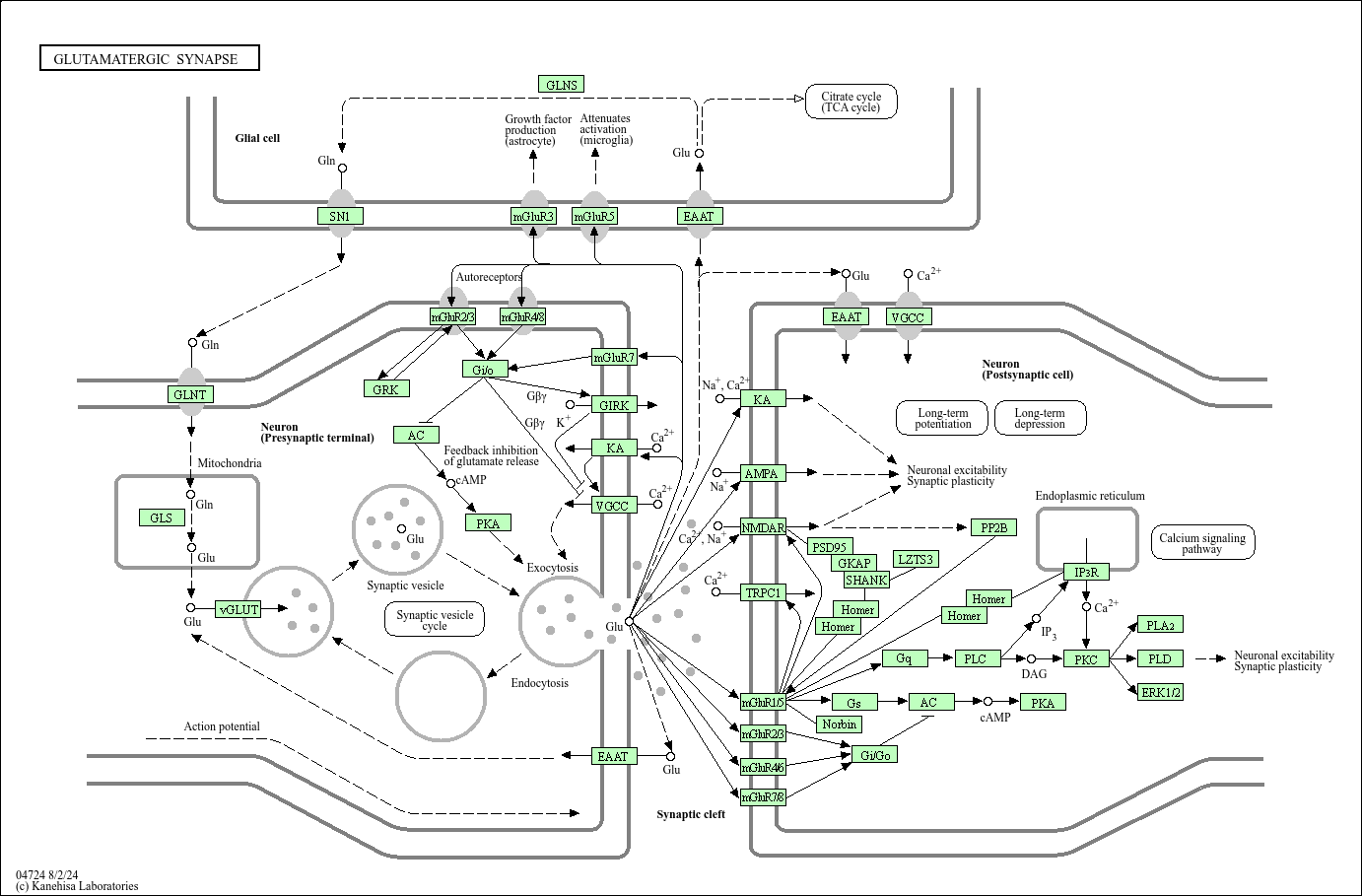
Glutamatergic synapse
Core of basic research: Deciphers the synaptic transmission mechanism of glutamate (Glu) as the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, participating in learning/memory, neural development, synaptic plasticity, and pain conduction. Glu released by presynaptic neurons binds to postsynaptic glutamate receptors, divided into ionotropic (iGluR) and metabotropic (mGluR) receptors: iGluRs include AMPA, NMDA, and kainate receptors; AMPA receptors rapidly mediate sodium influx to generate excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSP); NMDA receptors are voltage-dependent calcium channels, activated only when postsynaptic membranes are depolarized (relieving Mg²⁺ blockage) to mediate calcium influx, participating in synaptic plasticity (e.g., long-term potentiation/LTP, the molecular basis of learning/memory); mGluRs (mGluR1-mGluR8) regulate downstream signals via G proteins (PLC-γ or inhibiting AC) to modulate synaptic transmission strength and neural excitability. Glu in the synaptic cleft is reuptaken by presynaptic neurons or glial cells via excitatory amino acid transporters (EAAT) to terminate signals. Research focuses on the voltage-dependent activation mechanism of NMDA receptors, the association between AMPA receptor membrane trafficking and synaptic plasticity, excitotoxicity induced by excessive Glu release (e.g., cerebral ischemia, epilepsy), and pathway abnormalities in neurodegenerative diseases (Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease).
Core key proteins: Glutamate (Glu), ionotropic glutamate receptors (AMPA, NMDA, kainate), metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR1-mGluR8), EAAT (excitatory amino acid transporters, EAAT1-EAAT5), Synaptotagmin (regulating synaptic vesicle exocytosis), Ca²⁺ (calcium ion), CaMKII (calmodulin-dependent kinase II, regulating synaptic plasticity), CREB (transcription factor involved in memory formation), PSD-95 (postsynaptic density protein anchoring NMDA receptors), NR2B (NMDA receptor subunit regulating calcium permeability), GluN1 (core NMDA receptor subunit).
Core key proteins: Glutamate (Glu), ionotropic glutamate receptors (AMPA, NMDA, kainate), metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR1-mGluR8), EAAT (excitatory amino acid transporters, EAAT1-EAAT5), Synaptotagmin (regulating synaptic vesicle exocytosis), Ca²⁺ (calcium ion), CaMKII (calmodulin-dependent kinase II, regulating synaptic plasticity), CREB (transcription factor involved in memory formation), PSD-95 (postsynaptic density protein anchoring NMDA receptors), NR2B (NMDA receptor subunit regulating calcium permeability), GluN1 (core NMDA receptor subunit).
Product list
-
{{item.title}}{{item.react}}{{item.applicat}}
Product list
Product name
Reactivity
Application
Related Resource Links
Related Promotional Journal Downloads

Explore Our Recommended Popular Products
More products
30,000+ high- quality products available online
Primary Antibodies, Secondary Antibodies, mIHC Kits, ELISA Kits, Proteins, Molecular Biology Products,Cell Lines,Reagents ...
Contact Us