- Home
- Products
- Pathway
- Support
- Contact Us

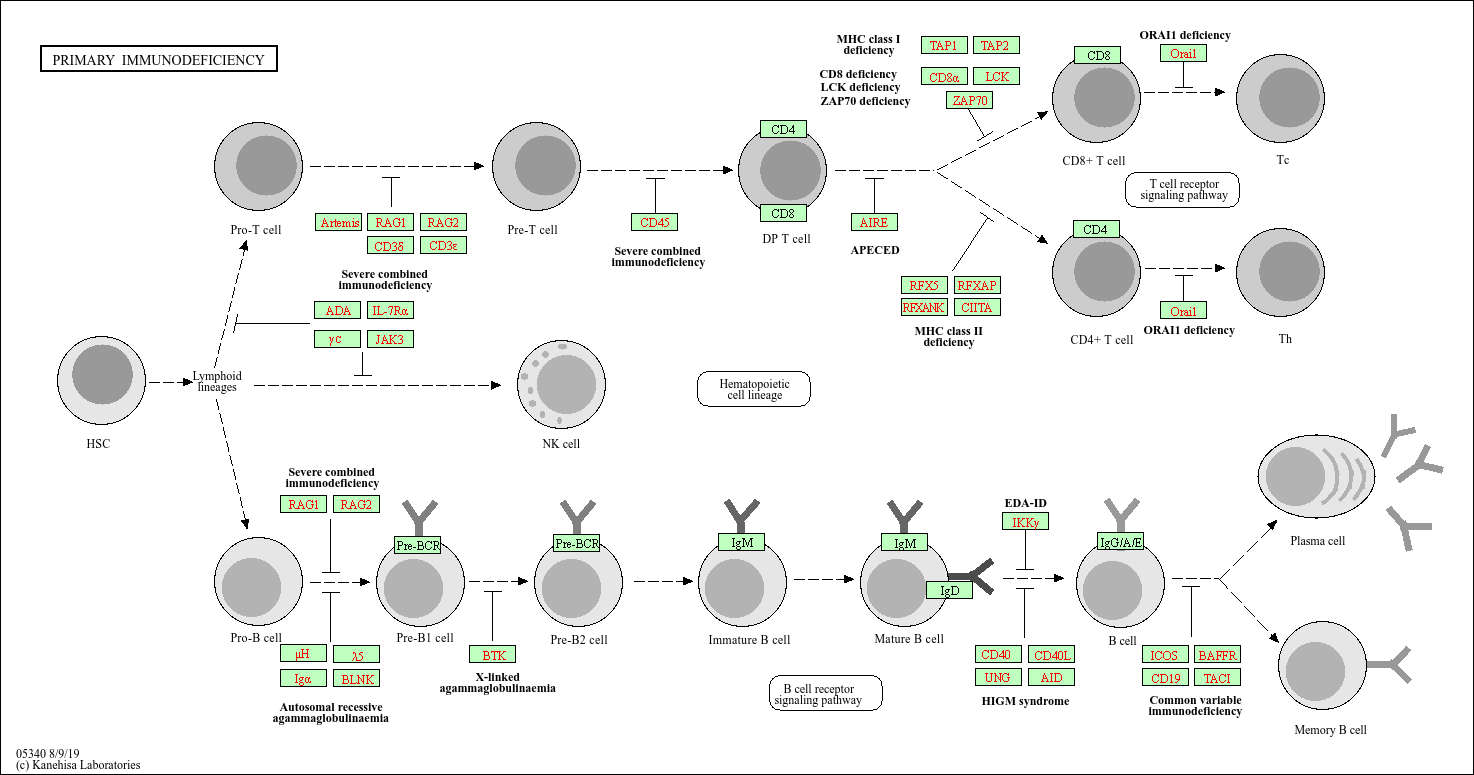
Primary immunodeficiency
Core of basic research: Clarify the genetic mechanisms of developmental, activation, or functional defects in immune cells (T/B cells, complement), focus on the impact of mutations in key genes (ADA, BTK, IL-2Rγ) on the immune network, providing a theoretical basis for gene therapy and replacement therapy.
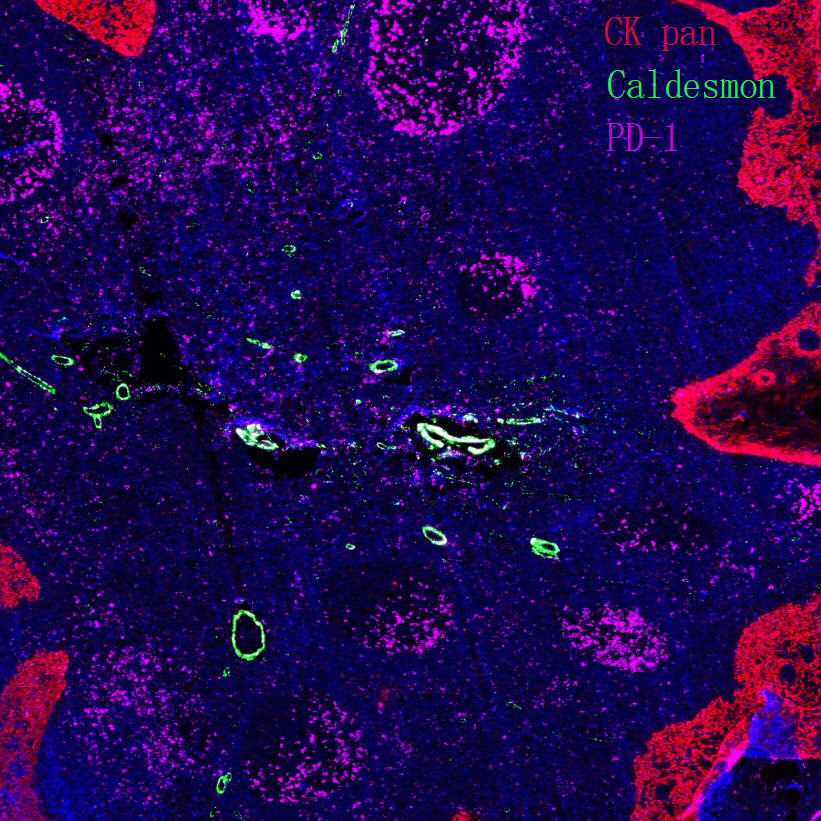
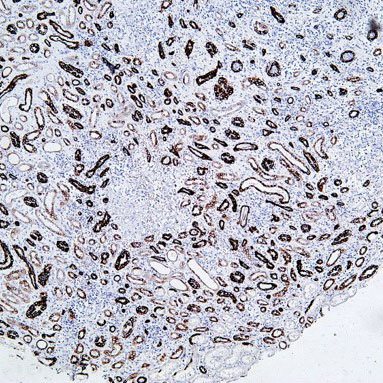
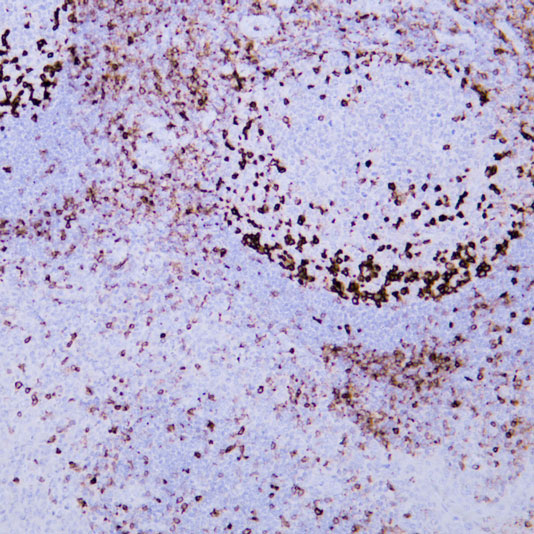
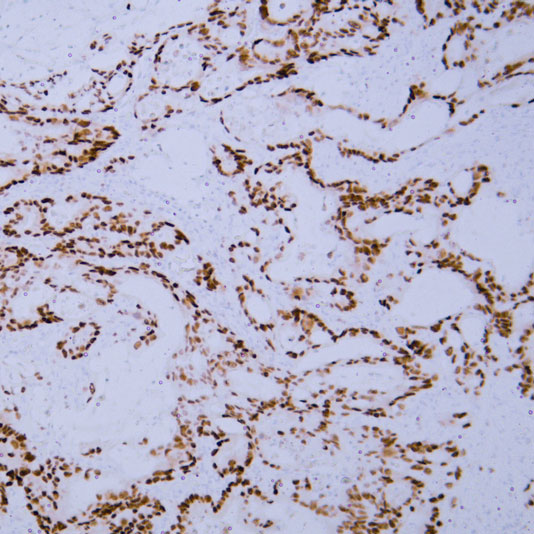
Core key proteins: ADA (adenosine deaminase, deficiency causes T/B cell developmental disorders), IL-2Rγ (cytokine receptor subunit, deficiency causes severe combined immunodeficiency), BTK (Bruton tyrosine kinase, deficiency causes B cell maturation disorders), CD40L (T cell surface molecule, deficiency impairs B cell activation), STAT3 (signal factor, deficiency causes immune cell dysfunction), PI3K (signaling pathway, deficiency affects immune cell activation), MHC-II (antigen-presenting molecule, deficiency causes immune response defects), Complement components (C3/C5, deficiency increases susceptibility to infections).
Core key proteins: ADA (adenosine deaminase, deficiency causes T/B cell developmental disorders), IL-2Rγ (cytokine receptor subunit, deficiency causes severe combined immunodeficiency), BTK (Bruton tyrosine kinase, deficiency causes B cell maturation disorders), CD40L (T cell surface molecule, deficiency impairs B cell activation), STAT3 (signal factor, deficiency causes immune cell dysfunction), PI3K (signaling pathway, deficiency affects immune cell activation), MHC-II (antigen-presenting molecule, deficiency causes immune response defects), Complement components (C3/C5, deficiency increases susceptibility to infections).
Product list
-
{{item.title}}{{item.react}}{{item.applicat}}
Product list
Product name
Reactivity
Application
Related Resource Links
Related Promotional Journal Downloads

Explore Our Recommended Popular Products
More products
30,000+ high- quality products available online
Primary Antibodies, Secondary Antibodies, mIHC Kits, ELISA Kits, Proteins, Molecular Biology Products,Cell Lines,Reagents ...
Contact Us