- Home
- Products
- Pathway
- Support
- Contact Us

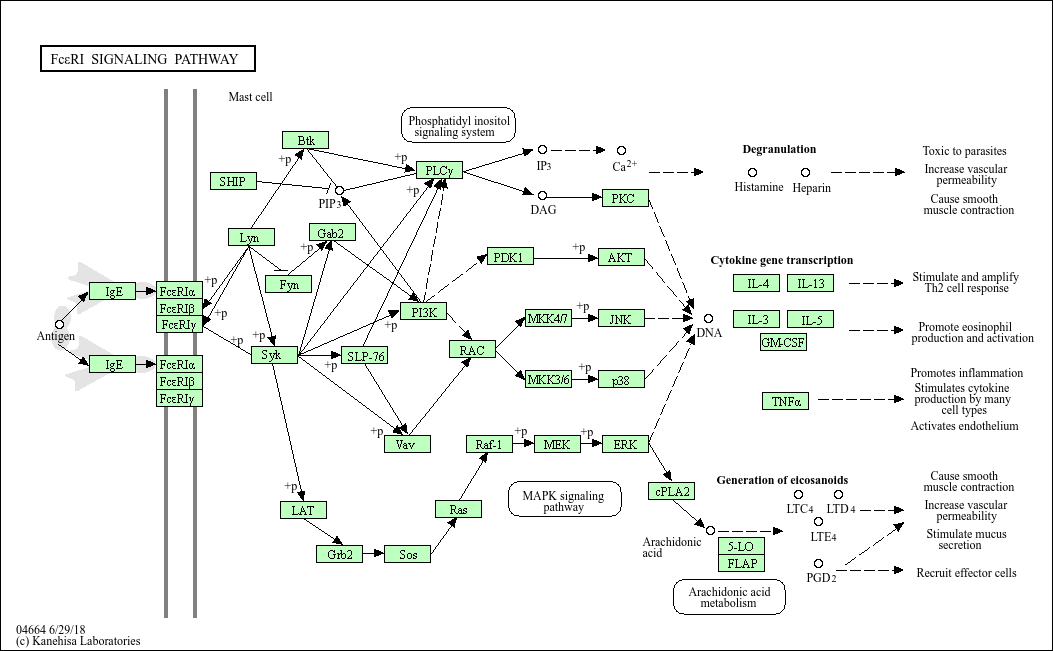
Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway
Core of basic research: As a core pathway for allergic reactions and anti-parasitic infections, it focuses on the activation mechanism of mast cells and basophils mediated by IgE cross-linking FcεRI. FcεRI consists of α, β, and γ chains, with the α chain binding IgE and the γ chain containing ITAM motifs. When multivalent antigens cross-link adjacent IgE, FcεRI aggregates, and Lyn kinase phosphorylates the γ chain ITAM, recruiting and activating Syk kinase. This further activates PLC-γ1, promoting IP3 production and calcium influx, triggering mast cell degranulation to release pre-stored mediators such as histamine and heparin, while synthesizing and secreting cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-4 via the MAPK and NF-κB pathways. Research focuses on the threshold regulation of signal activation (to avoid excessive allergic reactions), the association mechanism between calcium influx and degranulation, the role of negative regulators (e.g., SHP-1), and the molecular basis of abnormal pathway activation in allergic diseases (e.g., asthma, urticaria).
Core key proteins: FcεRI (α/β/γ chains), Lyn, Syk (tyrosine kinases), PLC-γ1, IP3R (endoplasmic reticulum calcium channel), PKC, MAPK (ERK/JNK), NF-κB, histamine, TNF-α, IL-4, SHP-1 (negative regulator), Gab2 (signal adaptor protein).
Core key proteins: FcεRI (α/β/γ chains), Lyn, Syk (tyrosine kinases), PLC-γ1, IP3R (endoplasmic reticulum calcium channel), PKC, MAPK (ERK/JNK), NF-κB, histamine, TNF-α, IL-4, SHP-1 (negative regulator), Gab2 (signal adaptor protein).
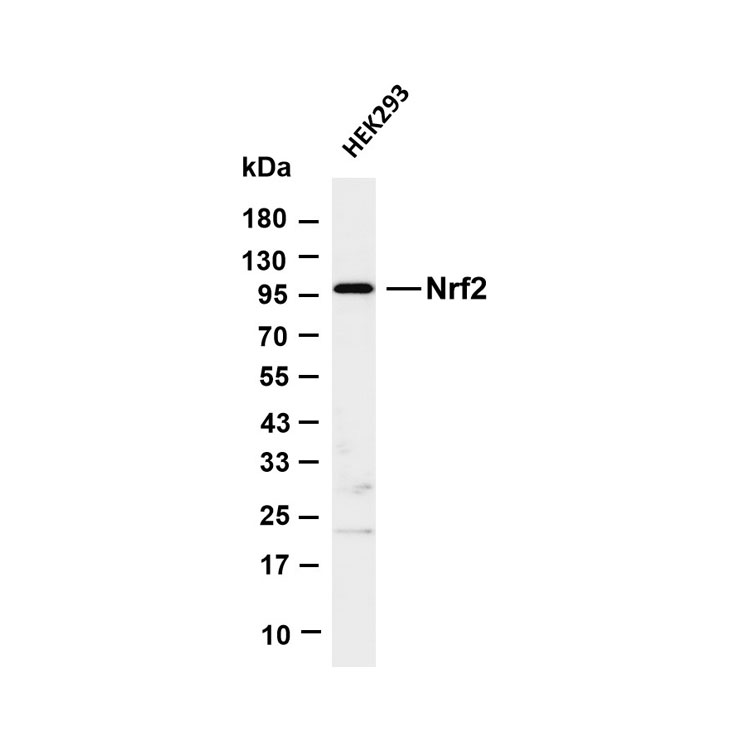
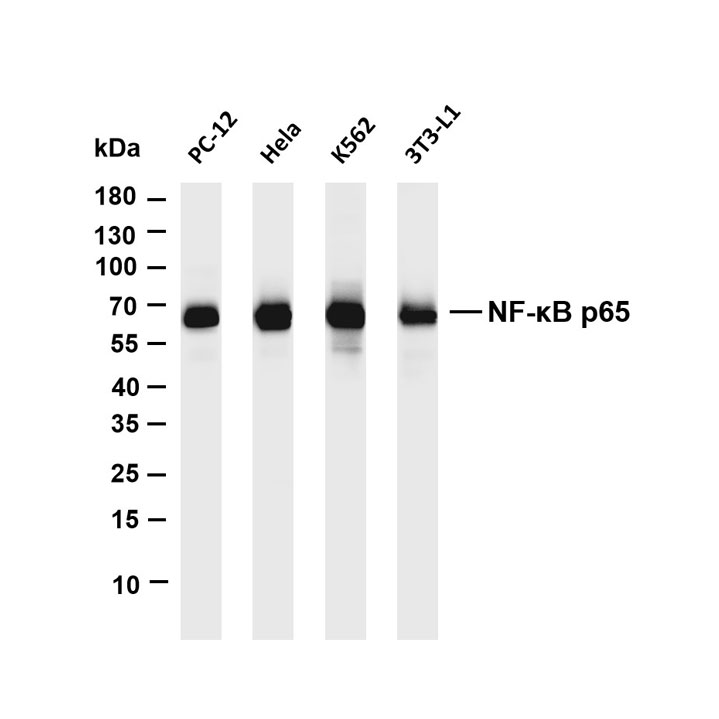
Product list
-
{{item.title}}{{item.react}}{{item.applicat}}
Product list
Product name
Reactivity
Application
Related Resource Links
Related Promotional Journal Downloads

Explore Our Recommended Popular Products
More products
30,000+ high- quality products available online
Primary Antibodies, Secondary Antibodies, mIHC Kits, ELISA Kits, Proteins, Molecular Biology Products,Cell Lines,Reagents ...
Contact Us