- Home
- Products
- Pathway
- Support
- Contact Us

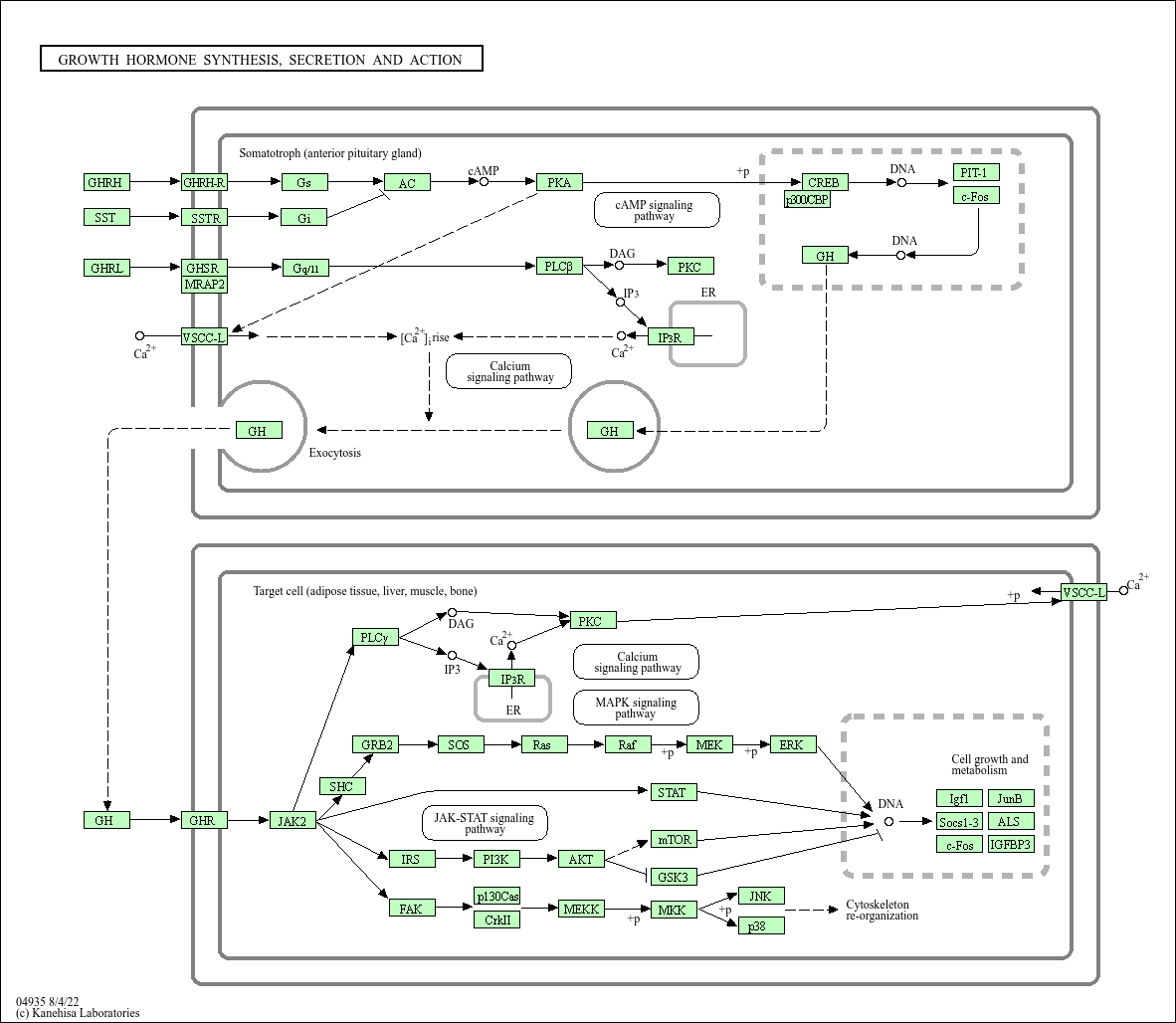
Growth hormone synthesis, secretion and action
Core of basic research: Clarifies the molecular mechanisms of growth hormone (GH) synthesis and secretion by somatotrophs in the anterior pituitary, and GH-mediated regulation of growth and development as well as metabolic remodeling. GH secretion is dually regulated by hypothalamic GHRH and somatostatin (SS): GHRH binds to its receptor to activate the cAMP-PKA pathway, promoting GH gene transcription and secretion; SS inhibits GH secretion by suppressing cAMP production. GH binds to the growth hormone receptor (GHR) on target cells (liver, bone, muscle), inducing receptor dimerization and recruiting JAK2 kinase to activate the JAK2-STAT5 pathway, promoting IGF-1 synthesis. IGF-1 binds to IGF-1R to further activate the PI3K-Akt and MAPK pathways, promoting chondrocyte proliferation (bone growth), protein synthesis, and lipolysis. Research focuses on the rhythmic regulation of GH secretion, the GHRH-SS balance mechanism, and pathway abnormalities associated with dwarfism (GH deficiency), gigantism (excessive GH), and metabolic disorders.
Core key proteins: GH (growth hormone), GHRH (growth hormone-releasing hormone), SS (somatostatin), IGF-1 (insulin-like growth factor 1), GHR (growth hormone receptor), IGF-1R (IGF-1 receptor), JAK2, STAT5, PI3K, Akt, MAPK (ERK), GHRHR (GHRH receptor), SSTR (somatostatin receptor), CYP19A1 (aromatase), chondrocytes/osteoblasts (target cells).
Core key proteins: GH (growth hormone), GHRH (growth hormone-releasing hormone), SS (somatostatin), IGF-1 (insulin-like growth factor 1), GHR (growth hormone receptor), IGF-1R (IGF-1 receptor), JAK2, STAT5, PI3K, Akt, MAPK (ERK), GHRHR (GHRH receptor), SSTR (somatostatin receptor), CYP19A1 (aromatase), chondrocytes/osteoblasts (target cells).
Product list
-
{{item.title}}{{item.react}}{{item.applicat}}
Product list
Product name
Reactivity
Application
Related Resource Links
Related Promotional Journal Downloads

Explore Our Recommended Popular Products
More products
30,000+ high- quality products available online
Primary Antibodies, Secondary Antibodies, mIHC Kits, ELISA Kits, Proteins, Molecular Biology Products,Cell Lines,Reagents ...
Contact Us