- Home
- Products
- Pathway
- Support
- Contact Us

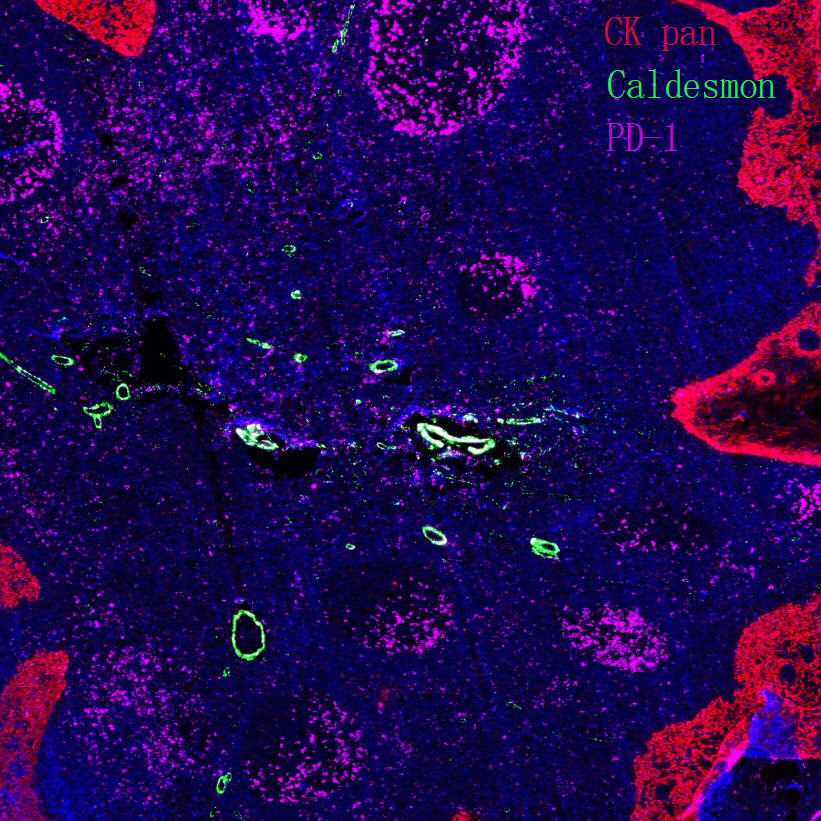
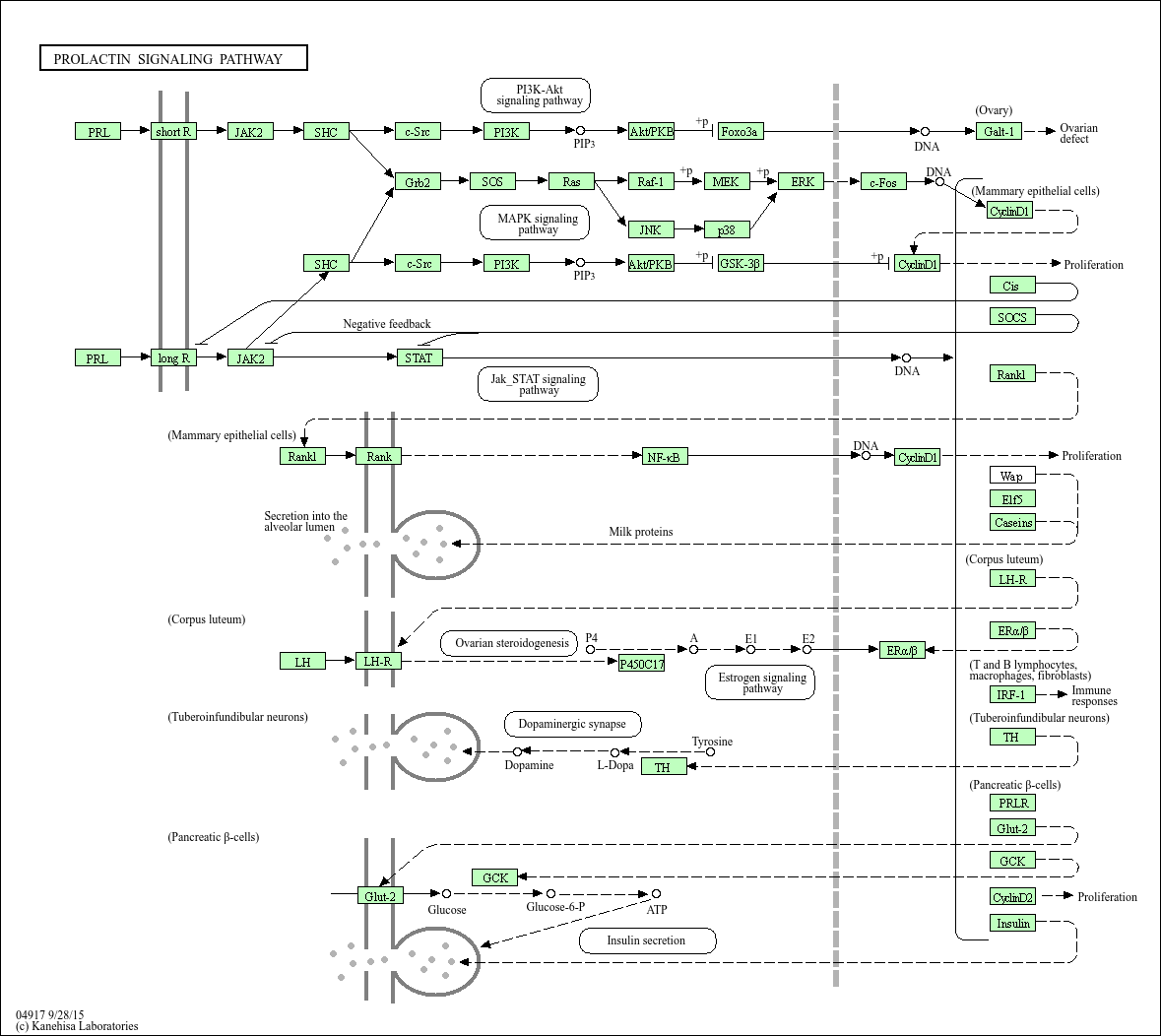
Prolactin signaling pathway
Core of basic research: Deciphers the molecular mechanism by which prolactin (PRL) regulates mammary gland development, lactation, and reproductive function, a key pathway for mammalian reproduction and lactation. PRL is synthesized and secreted by anterior pituitary lactotrophs, negatively regulated by hypothalamic dopamine (DA) (DA binds D2 receptors to inhibit PRL secretion). PRL binding to prolactin receptors (PRLR) on target cells (mammary epithelial cells, gonadal cells) induces receptor dimerization and recruitment of JAK2 kinase, which autophosphorylates and phosphorylates the PRLR cytoplasmic domain, further phosphorylating STAT5. Phosphorylated STAT5 forms dimers, translocates to the nucleus, and binds to STAT-binding elements in target genes (e.g., β-casein, whey acidic protein) to activate lactation-related gene transcription. Additionally, PRL activates the PI3K-Akt and MAPK pathways to promote mammary epithelial cell proliferation and survival. Research focuses on the regulatory balance of DA on PRL secretion, activation and regulation of the JAK2-STAT5 pathway, the transcriptional regulatory network of lactation genes, and pathway abnormalities in mammary hyperplasia, breast cancer, and hyperprolactinemia.
Core key proteins: Prolactin (PRL), prolactin receptor (PRLR), JAK2 (tyrosine kinase), STAT5 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 5), β-casein/whey acidic protein (lactation-related target genes), PI3K/Akt (proliferation and survival signaling pathway), MAPK (ERK, mitogen-activated protein kinase), dopamine (DA, negative regulator), D2 receptor (dopamine receptor), SOCS1/SOCS3 (suppressors of cytokine signaling, negative regulators), Cyclin D1 (cell cycle protein, promotes proliferation), mammary epithelial cells.
Core key proteins: Prolactin (PRL), prolactin receptor (PRLR), JAK2 (tyrosine kinase), STAT5 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 5), β-casein/whey acidic protein (lactation-related target genes), PI3K/Akt (proliferation and survival signaling pathway), MAPK (ERK, mitogen-activated protein kinase), dopamine (DA, negative regulator), D2 receptor (dopamine receptor), SOCS1/SOCS3 (suppressors of cytokine signaling, negative regulators), Cyclin D1 (cell cycle protein, promotes proliferation), mammary epithelial cells.
Product list
-
{{item.title}}{{item.react}}{{item.applicat}}
Product list
Product name
Reactivity
Application
Related Resource Links
Related Promotional Journal Downloads

Explore Our Recommended Popular Products
More products
30,000+ high- quality products available online
Primary Antibodies, Secondary Antibodies, mIHC Kits, ELISA Kits, Proteins, Molecular Biology Products,Cell Lines,Reagents ...
Contact Us