- Home
- Products
- Pathway
- Support
- Contact Us

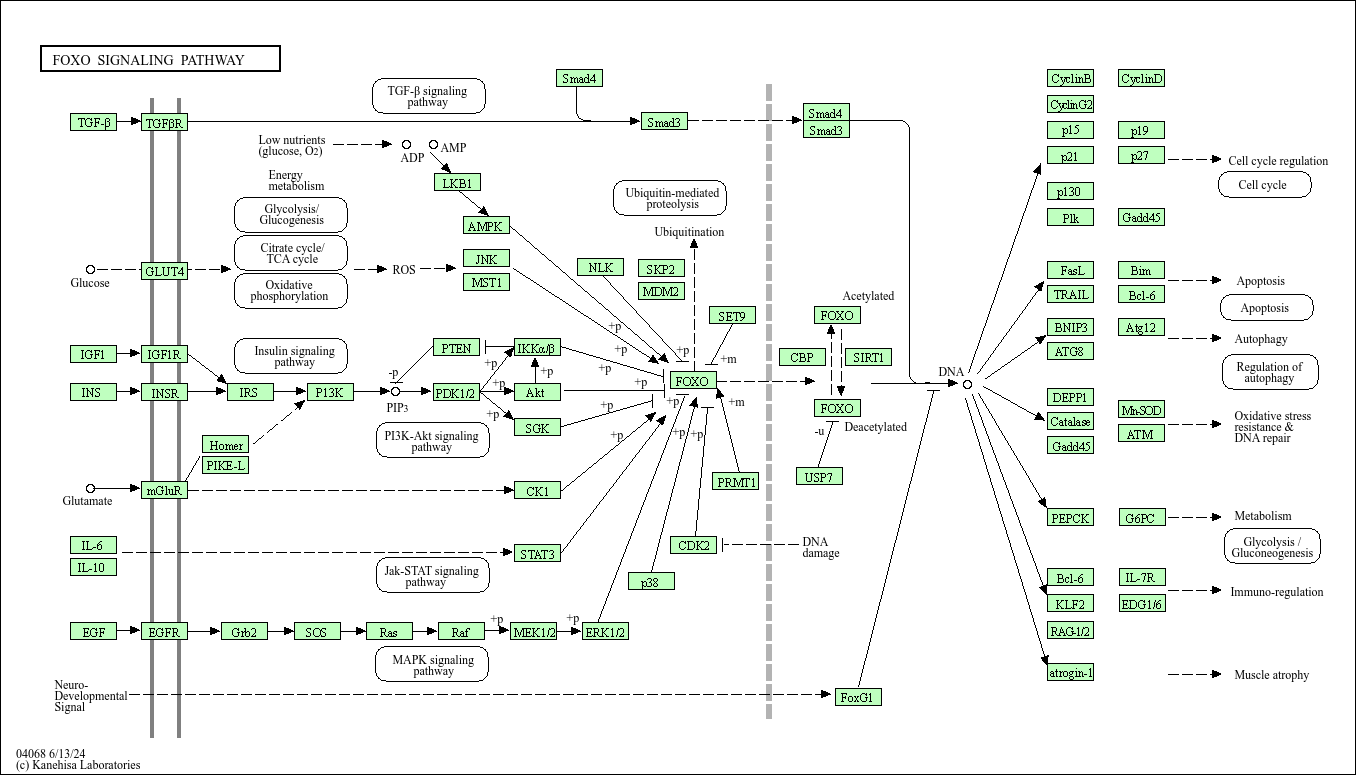
FoxO signaling pathway
Centered on transcription factors such as FoxO1, FoxO3, FoxO4, and FoxO6, it participates in the regulation of cell fate by controlling the expression of downstream target genes. The activity of FoxO proteins is strictly regulated by phosphorylation: phosphorylation by kinases such as Akt and SGK retains them in the cytoplasm and inactivates them; phosphorylation by AMPK and JNK promotes their nuclear translocation and activation of target genes. The core target genes regulated are involved in cell cycle arrest (p21, p27), apoptosis (Bim, FasL), oxidative stress resistance (SOD2, CAT), and metabolic balance (G6Pase, PEPCK). It plays a role in maintaining cellular homeostasis, delaying aging, and inhibiting tumors. Pathway dysfunction is associated with tumors, metabolic syndrome, and neurodegenerative diseases; for example, FoxO3 inactivation is related to the progression of breast cancer and prostate cancer.
Core function: Regulate cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, differentiation, and metabolism through FoxO transcription factors to maintain cellular and tissue homeostasis. Key regulatory molecules: FoxO1/3/4/6, Akt, AMPK, mTOR, ROS.
Core function: Regulate cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, differentiation, and metabolism through FoxO transcription factors to maintain cellular and tissue homeostasis. Key regulatory molecules: FoxO1/3/4/6, Akt, AMPK, mTOR, ROS.
Product list
-
{{item.title}}{{item.react}}{{item.applicat}}
Product list
Product name
Reactivity
Application
Related Resource Links
Related Promotional Journal Downloads

Explore Our Recommended Popular Products
More products
30,000+ high- quality products available online
Primary Antibodies, Secondary Antibodies, mIHC Kits, ELISA Kits, Proteins, Molecular Biology Products,Cell Lines,Reagents ...
Contact Us